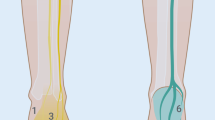
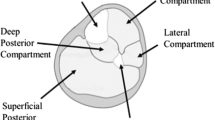
Abstract
Exercise-related leg pain is a common and yet difficult management problem in sports medicine. There are many common causes of such symptoms including stress fractures and muscle compartment syndromes. There are also a number of less common but important conditions including popliteal artery entrapment and nerve entrapment syndromes. Even for an astute clinician, distinction between the different medical causes may be difficult given that many of their presenting features overlap. This review highlights the common clinical presentations and raises a regional approach to the diagnosis of the neurogenic symptoms. In part, this overlapping presentation of different pathological conditions may be due to a common aetiological basis of many of these conditions namely, fascial dysfunction. The same fascial restriction that predisposes to muscle compartment syndromes may also envelop the neurovascular structures within the leg resulting in either ischaemic or neurogenic symptoms. For many athletes with chronic exercise-related leg pain, combinations of such problems often coexist suggesting a more widespread fascial pathology. In our clinical experience, we often label such patients as ’fasciopaths’; however, the precise pathophysiological basis of this fascial problem remains to be elucidated. This review discusses the various nerve entrapment syndromes in the lower limb that may result in exercise-related leg pain in the sporting context. The anatomy, clinical presentation, investigation, medical management and surgical treatment are discussed at length for each of the syndromes. It is clear from clinical experience that the outcome of surgical management of such syndromes fares much better where a clear dermatomal pain distribution is present or where focal weakness and/or sensory symptoms appropriate for the nerve are present. In many situations, however, nonspecific leg pain or vague nonlocalising sensory symptoms are present and in such situations, alternative diagnoses must be considered and investigated appropriately. As mentioned above, many different pathologies may coexist in the lower limb and may be a source of confusion for the clinician or alternatively may be the reason for poor treatment outcomes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peri G. The ’critical zones’ of entrapment of the nerves of the lower limb. Surg Radiol Anat 1991; 13 (2): 139–43
McCluskey LF, Webb LB. Compression and entrapment neuropathies of the lower extremity. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1999; 16 (1): 97–125, vii
Schon L, Baxter D. Neuropathies of the foot and ankle in athletes. Clin Sports Med 1990; 9 (2): 489–509
Baxter DE. Functional nerve disorders in the athlete’s foot, ankle, and leg. Instr Course Lect 1993; 42: 185–94
Fernandez E, Pallini R, Lauretti L, et al. Neurosurgery of the peripheral nervous system: entrapment syndromes of the lower extremity. Surg Neurol 1999; 52 (5): 449–52
Biundo Jr JJ, Harris MA. Peripheral nerve entrapment, occupation related syndromes and sports injuries, and bursitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1993; 5 (2): 224–9
Bickerstaff E, Spillane J. Neurological examination in clinical practice. 5th ed. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1989
Wilbourne A. Electrodiagnostic testing of neurologic injuries in athletes. Clin Sports Med 1990; 9: 229–45
Stewart J. Focal peripheral neuropathies. 3rd ed. New York: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2000
Martinoli C, Bianchi S, Gandolfo N, et al. US of nerve entrapments in osteofibrous tunnels of the upper and lower limbs. Radiographics 2000; 20 Spec No.: S199–213
Erickson S, Quinn S, Kneeland J. MR imaging of the tarsal tunnel and related spaces: normal and abnormal findings with anatomical correlation. Am J Roentgenol 1990; 155: 323–8
Pecina M, Krmpotic-Nemanic J, Markiewitz A. Tunnel syndromes: peripheral nerve compression syndromes. 3rd ed. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press, 2001
Kopell HP, Thompson W. Peripheral nerve entrapments of the lower extremity. New Engl J Med 1962; 266: 16–9
Kopell H, Thompson W. Peripheral entrapment neuropathies. Baltimore (MD): Williams and Wilkins, 1963
Deese J, Baxter D. Compressive neuropathies of the lower extremity. J Musculoskel Med 1988; 5: 678–95
Dumitru D, Windsor R. Subsartorial entrapment of the saphenous nerve of a competitive female bodybuilder. Physician Sportsmed 1989; 17: 116–25
Worth R, Kettelkamp DB, Defalque R, et al. Saphenous nerve entrapment: a cause of medial knee pain. Am J Sports Med 1984; 12: 80–1
Wartenberg R. Digitalia paraestetica and gonialgia paraesthetica. Neurology 1953; 4: 106–16
Senegor M. Iatrogenic saphenous neuralgia. Neurosurgery 1991; 28: 295–8
McCrory P, Bell S. Nerve entrapment syndromes as a cause of pain in the hip, groin and buttock. Sports Med 1999; 27: 261–74
Akyuz G, Us O, Turan B, et al. Anterior tarsal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 2000; 40 (2): 123–8
Mumenthaler M, Schliack H. Peripheral nerve lesions: diagnosis and therapy. New York: Thieme, 1991
Leach R, Purnell M, Saito A. Peroneal nerve entrapment in runners. Am J Sports Med 1989; 17: 287–91
Moller B, Kadin S. Entrapment of the common peroneal nerve. Am J Sports Med 1987; 15: 90–1
Stack R, Bianco A, McCarty C. Compression of the common peroneal nerve by ganglion cysts. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1965; 47: 773–8
Fabre T, Piton C, Andre D, et al. Peroneal nerve entrapment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1998; 80 (1): 47–53
Styf J. Entrapment of the superficial peroneal nerve: diagnosis and results of decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1989; 71: 131–5
Styf J, Korner I. Chronic anterior compartment syndrome of the leg. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1986; 68: 1338–47
Styf J. Chronic exercise-induced pain in the anterior aspect of the lower leg: an overview of the diagnosis. SportsMed 1989; 7: 331–9
Levin K, Stevens J, Daube J. Superficial peroneal nerve conduction studies for electromyographic diagnosis. Muscle Nerve 1986; 9: 322–6
Adelman K, Wilson G, Wolf J. Anterior tarsal tunnel syndrome. J Foot Surg 1988; 27: 299–302
Parks A. Intraneural ganglion of the lateral popliteal nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1961; 43: 784–90
Muckart R. Compression of the common peroneal nerve by intramuscular ganglion from the superior tibio-fibular joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1976; 58: 241–4
Evans J, Neumann L, Frostick S. Compression neuropathy of the common peroneal nerve caused by a ganglion. Microsurgery 1994; 15: 193–5
Kernohan J, Levack B, Wilson J. Entrapment of the superficial peroneal nerve: three case reports. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1985; 67: 60–1
Styf J, Morberg G. Superficial peroneal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1997; 79: 801–7
Johnston E, Howell S. Tension neuropathy of the superficial peroneal nerve: associated conditions and response to surgical release. Foot Ankle Int 1999; 20 (9): 576–82
Daniels T, Lau J, Hearn T. The effects of foot position and load on tibial nerve tension. Foot Ankle Int 1998; 19 (2): 73–8
Williams D. A study of the human medial peroneal nerve, a new name proposed for the peroneal anastomotic nerve. Anat Rec 1954; 118: 415–21
Coert J, Dellon A. Clinical implications of the surgical anatomy of the sural nerve. Plast Reconstr Surg 1994; 94: 850–5
Pringle R, Protheroe K, Mukherjee S. Entrapment neuropathy of the sural nerve. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1974; 56: 465–8
Schon L. Nerve entrapment, neuropathy and nerve dysfunction in athletes. Orthop Clin North Am 1994; 25: 47–59
Schuchmann J. Isolated sural neuropathy: report of two cases. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1980; 61: 313–29
Aszmann OC, Ebmer JM, Dellon AL. Cutaneous innervation of the medial ankle: an anatomic study of the saphenous, sural, and tibial nerves and their clinical significance. Foot Ankle Int 1998; 19 (11): 753–6
Dellon A, Mackinnon S. Tibial nerve branching in the tarsal tunnel. Arch Neurol 1984; 41: 645–6
Nagaoka M. An anatomical study of the tarsal tunnel. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 1990; 64: 208–16
Baxter DE, Pfeffer GB. Treatment of chronic heel pain by surgical release of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve. Clin Orthop 1992 Jun; (279): 229–36
Campbell P, Lawton JO. Heel pain: diagnosis and management. Br J Hosp Med 1994; 52 (8): 380–5
Goecker RM, Banks AS. Analysis of release of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2000; 90 (6): 281–6
Hendrix CL, Jolly GP, Garbalosa JC, et al. Entrapment neuropathy: the etiology of intractable chronic heel pain syndrome. J Foot Ankle Surg 1998; 37 (4): 273–9
Pfeffer GB. Plantar heel pain. Instr Course Lect 2001; 50: 521–31
Oh SJ, Kwon KH, Hah JS, et al. Lateral plantar neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 1999; 22 (9): 1234–8
McMaster WC. How can chronic heel pain be treated? Postgrad Med 2001; 109 (4): 137–8
Oh SJ, Meyer RD. Entrapment neuropathies of the tibial (posterior tibial) nerve. Neurol Clin 1999; 17 (3): 593–615, vii
Kashani S, Moon A, Gaunt W. Tibial nerve entrapment by a Baker’s cyst. Arch Phys Med Rehab 1985; 66: 49–51
Donell S, Barrett D. Entrapment neuropathies. Part 2: lower limb. Br J Hosp Med 1991; 46: 99–101
Nakano K. The entrapment neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 1978; 1: 264–79
Stewart J. Medial plantar neuropathy. Neurology 1981; 31: 149
Baxter D. Compressive neuropathies of the foot and ankle. Oper Tech Sports Med 1994; 2: 18–23
Oh S, Lee K. Medial plantar neuropathy. Neurology 1987; 37: 1408–10
Fredericson M, Standage S, Chou L, et al. Lateral plantar nerve entrapment in a competitive gymnast. Clin J Sport Med 2001; 11 (2): 111–4
Hah J, Kim D. Lateral plantar neuropathy: a heretofore unrecognised neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 1992; 15: 1175
Brooks D. Nerve compression by simple ganglia: a review of thirteen collected cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1952; 34: 391–400
Cerciello M, Napoleoni F. The tarsal tunnel syndrome [in Italian]. Riv Eur Sci Med Farmacol 1991; 13 (1–2): 61–9
Trepman E, Kadel N, Chisholm K, et al. Effect of foot and ankle position on tarsal tunnel compartment pressure. Foot Ankle Int 1999; 20 (11): 721–6
Marinacci A. Neurological syndromes of the tarsal tunnels. Bull Los Angeles Neurol Soc 1968; 33: 90–100
Edwards W, Lincoln C, Basset F. The tarsal tunnel syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. JAMA 1969; 207: 716–20
Keck C. The tarsal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1962; 44: 180–2
Linscheid R, Burton R, Fredericks E. Tarsal tunnel syndrome. South Med J 1970; 63: 1313–23
Pace N, Serafini P, LoIocano E, et al. The tarsal and calcaneal tunnel syndromes. Ital J Orthop Traumatol 1991; 17: 247–52
Jackson D, Haglund B. Tarsal tunnel syndrome in athletes: case reports and literature review. Am J Sports Med 1991; 19: 61–5
Jackson D, Haglund B. Tarsal tunnel syndrome in runners. Sports Med 1992; 13: 146–9
Park TA, Del Toro DR. Electrodiagnostic evaluation of the foot. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 1998; 9 (4): 871–96, vii-viii
Johnson E, Ortiz P. Electrodiagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1966; 47: 776–80
Fu R, DeLisa J, Kraft G. Motor nerve latencies through the tarsal tunnel in normal adult subjects. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1980; 61: 243–8
David WS, Doyle JJ. Segmental near nerve sensory conduction studies of the medical and lateral plantar nerve. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 1996; 36 (7): 411–7
de Bisschop G, Claparede P, Bence YR, et al. Neuromuscular study of the foot: value of electromyographic and neuronographic examinations [in French]. Electrodiagn Ther 1979; 16 (2): 77–86
Zeiss J, Ebraheim N, Rusin J. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of tarsal tunnel syndrome: case report. Clin Imaging 1990; 14: 123–6
Frey C, Kerr R. Magnetic resonance imaging and the evaluation of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Foot Ankle 1993; 14 (3): 159–64
Cheung YY, Rosenberg ZS, Colon E, et al. MR imaging of flexor digitorum accessorius longus. Skeletal Radiol 1999; 28 (3): 130–7
Rosenberg ZS, Beltran J, Bencardino JT. From the RSNA Refresher Courses. Radiological Society of North America: MR imaging of the ankle and foot. Radiographics 2000; 20 Spec. No.: S153–79
Carrel JM, Davidson DM, Goldstein KT. Observations on 200 surgical cases of tarsal tunnel syndrome. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1994; 11 (4): 609–16
Ward PJ, Porter ML. Tarsal tunnel syndrome: a study of the clinical and neurophysiological results of decompression. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1998; 43 (1): 35–6
Davis A, Schon L. Branches of the tibial nerve: anatomic variations. Foot Ankle Int 1995; 16: 21–9
De Palma L, Tulli A. Morton’s disease: optic and electron microscopy observations [in French]. Acta Orthop Belg 1991; 57 (3): 285–95
Lassmann G, Lassmann H, Stockinger L. Morton’s metatarsalgia: light and electron microscopic observations and their relation to entrapment neuropathies. Virchows Arch 1976; 370: 307–21
Falck B, Hurme M, Hakkarainen S. Sensory conduction velocity of plantar digital nerves in Morton’s metatarsalgia. Neurology 1984; 34: 698–701
Oh S, Kim H, Ahmad B. Electrophysiological diagnosis of interdigital neuropathy of the foot. Muscle Nerve 1984; 7: 218–115
Redd R, Peters V, Emery S, et al. Morton’s neuroma: sonographic evaluation. Radiology 1989; 171: 415–6
Bennett GL, Graham CE, Mauldin DM. Morton’s interdigital neuroma: a comprehensive treatment protocol. Foot Ankle Int 1995; 16 (12): 760–3
Greenfield J, Rea J, Ilfeld F. Morton’s interdigital neuroma: indications for treatment by local injections versus surgery. Clin Orthop 1984; 185: 142–4
Gaynor R, Hake D, Spinner S, et al. A comparative analysis of conservative versus surgical treatment of Morton’s neuroma. J Am Podiatr Assoc 1989; 79: 27–30
Dellon AL. Treatment of Morton’s neuroma as a nerve compression: the role for neurolysis. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 1992; 82 (8): 399–402
Nashi M, Venkatachalam AK, Muddu BN. Surgery of Morton’s neuroma: dorsal or plantar approach? J R Coll Surg Edinb 1997; 42 (1): 36–7
Still GP, Fowler MB. Joplin’s neuroma or compression neuropathy of the plantar proper digital nerve to the hallux: clinicopathologic study of three cases. J Foot Ankle Surg 1998; 37 (6): 524–30
Ames P, Lenet M, Sherman M. Joplin’s neuroma. J Am Podiatr Assoc 1980; 70: 99–101
Joplin R. The proper digital nerve, vitallium stem arthroplasty and some thoughts about foot surgery in general. Clin Orthop 1971; 76: 199–212
Merritt G, Subotnick S. Medial plantar digital proper nerve syndrome (Joplin’s neuroma): typical presentation. J Foot Surg 1982; 21: 166–9
Jordan B, Tsaris P, Warren R, editors. Sports neurology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia (PA): Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1998
Bell S. Partial compartment fasciectomy as treatment for failed anterior compartment decompression. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1986; 68: 815–7
Acknowledgements
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCrory, P., Bell, S. & Bradshaw, C. Nerve Entrapments of the Lower Leg, Ankle and Foot in Sport. Sports Med 32, 371–391 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232060-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200232060-00003