Abstract
Rationale and objective
Empirical studies indicate that nicotine enhances some aspects of attention and cognition, suggesting a role in the maintenance of tobacco dependence. The purpose of this review was to update the literature since our previous review (Heishman et al. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2:345–395, 1994) and to determine which aspects of human performance were most sensitive to the effects of nicotine and smoking.
Methods
We conducted a meta-analysis on the outcome measures of 41 double-blind, placebo-controlled laboratory studies published from 1994 to 2008. In all studies, nicotine was administered, and performance was assessed in healthy adult nonsmokers or smokers who were not tobacco-deprived or minimally deprived (≤2 h).
Results
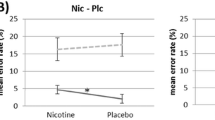
There were sufficient effect size data to conduct meta-analyses on nine performance domains, including motor abilities, alerting and orienting attention, and episodic and working memory. We found significant positive effects of nicotine or smoking on six domains: fine motor, alerting attention-accuracy and response time (RT), orienting attention-RT, short-term episodic memory-accuracy, and working memory-RT (effect size range = 0.16 to 0.44).
Conclusions
The significant effects of nicotine on motor abilities, attention, and memory likely represent true performance enhancement because they are not confounded by withdrawal relief. The beneficial cognitive effects of nicotine have implications for initiation of smoking and maintenance of tobacco dependence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
* Article met inclusion/exclusion criteria and was used in meta-analyses. † Article met inclusion/exclusion criteria but was not used in meta-analyses.
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed text revision. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Anstey KJ, von Sanden C, Salim A, O’Kearney R (2007) Smoking as a risk factor for dementia and cognitive decline: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am J Epidemiol 166:367–378
Azizian A, Monterosso J, O’Neill J, London ED (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging studies of cigarette smoking. Handb Exp Pharmacol 192:113–143
Baddeley AD (1999) Essentials of human memory. Psychology, Sussex
*Barr RS, Culhane MA, Jubelt LE, Mufti RS, Dyer MA, Weiss AP, Deckersbach T, Kelly JF, Freudenreich O, Goff DC, Evins AE (2008a) The effects of transdermal nicotine on cognition in nonsmokers with schizophrenia and nonpsychiatric controls. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:480–490
*Barr RS, Pizzagalli DA, Culhane MA, Goff DC, Evins AE (2008b) A single dose of nicotine enhances reward responsiveness in nonsmokers: implications for development of dependence. Biol Psychiatry 63:1061–1065
*Bates T, Mangan G, Stough C, Corballis P (1995) Smoking, processing speed and attention in a choice reaction time task. Psychopharmacology 120:209–212
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR (2009) Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley, Chichester
Brody AL (2006) Functional brain imaging of tobacco use and dependence. J Psychiatr Res 40:404–418
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009) Cigarette smoking among adults and trends in smoking cessation—United States, 2008. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 58:1227–1232
Cohen J (1960) A coefficient for agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas 20:37–46
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale
Cohen JD, Perlstein WM, Braver TS, Nystrom LE, Noll DC, Jonides J, Smith EE (1997) Temporal dynamics of brain activation during a working memory task. Nature 386:604–608
*Colzato LS, Fagioli S, Erasmus V, Hommel B (2005) Caffeine, but not nicotine, enhances visual feature binding. Eur J Neurosci 21:591–595
Coull JT, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ, Grasby PM (1996) A fronto-parietal network for rapid visual information processing: a PET study of sustained attention and working memory. Neuropsychologia 34:1085–1095
Dani JA, Bertrand D (2007) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:699–729
Debski EA (2008) Smoking, nicotine and visual plasticity: does what you know, tell you what you can see? Brain Res Bull 77:221–226
Di Matteo V, Pierucci M, Di Giovanni G, Benigno A, Esposito E (2007) The neurobiological bases for the pharmacotherapy of nicotine addiction. Curr Pharm Des 13:1269–1284
Egan TM, North RA (1986) Actions of acetylcholine and nicotine on rat locus coeruleus neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 19:565–571
Ellis J, Kvavilashvili L (2000) Prospective memory in 2000: past, present, and future directions. Appl Cogn Psychol 14:S1–S9
*Ernst M, Matochik JA, Heishman SJ, Van Horn JD, Jons PH, Henningfield JE, London ED (2001a) Effect of nicotine on brain activation during performance of a working memory task. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4728–4733
*Ernst M, Heishman SJ, Spurgeon L, London ED (2001b) Smoking history and nicotine effects on cognitive performance. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:313–319
Evans DE, Drobes DJ (2008) Nicotine self-medication of cognitive-attentional processing. Addict Biol 14:32–42
Fan J, McCandliss BD, Fossella J, Flombaum JI, Posner MI (2005) The activation of attentional networks. Neuroimage 18:14–57
Fan J, Gu X, Guise KG, Liu X, Fossella J, Wang H, Posner MI (2009) Testing the behavioral interaction and integration of attentional networks. Brain Cogn 70:209–220
*File SE, Fluck E, Leahy A (2001) Nicotine has calming effects on stress-induced mood changes in females, but enhances aggressive mood in males. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 4:371–376
Fiore MC, Jaén CR, Baker TB (2008) Treating tobacco use and dependence: 2008 update. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville
*Foulds J, Stapleton J, Swettenham J, Bell N, McSorley K, Russell MAH (1996) Cognitive performance effects of subcutaneous nicotine in smokers and never-smokers. Psychopharmacology 127:31–38
†Giessing C, Fink GR, Rösler F, Thiel CM (2007) fMRI data predict individual differences of behavioral effects of nicotine: a partial least square analysis. J Cogn Neurosci 19:658–670
*Griesar WS, Zajdel DP, Oken BS (2001) Nicotine effects on alertness and spatial attention in non-smokers. Nicotine Tob Res 4:185–194
*Hahn B, Ross TJ, Yang Y, Kim I, Huestis MA, Stein EA (2007) Nicotine enhances visuospatial attention by deactivating areas of the resting brain default network. J Neurosci 27:3477–3489
*Hahn B, Ross TJ, Wolkenberg FA, Shakleya DM, Huestis MA, Stein EA (2009) Performance effects of nicotine during selective attention, divided attention, and simple stimulus detection: an fMRI study. Cereb Cortex 19:1990–2000
*Harte CB, Kanarek RB (2004) The effects of nicotine and sucrose on spatial memory and attention. Nutr Neurosci 7:121–125
Heatherton TF, Kozlowski LT, Frecker RC, Fagerström KO (1991) The Fagerström test for nicotine dependence: a revision of the Fagerström Tolerance Questionnaire. Br J Addict 86:1119–1127
Hedges L, Olkin I (1985) Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Academic, San Diego
Heishman SJ (1998) What aspects of human performance are truly enhanced by nicotine? Addiction 93:317–320
*Heishman SJ, Henningfield JE (2000) Tolerance to repeated nicotine administration on performance, subjective, and physiological responses in nonsmokers. Psychopharmacology 152:321–333
Heishman SJ, Taylor RC, Henningfield JE (1994) Nicotine and smoking: a review of effects on human performance. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2:345–395
Hendricks PS, Ditre JW, Drobes DJ, Brandon TH (2006) The early time course of smoking withdrawal effects. Psychopharmacology 187:385–396
Henningfield JE, Shiffman S, Ferguson SG, Gritz ER (2009) Tobacco dependence and withdrawal: science base, challenges and opportunities for pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.03.011
Higgins J, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J 327:557–560
†Holmes AD, Chenery HJ, Copland DA (2008) Transdermal nicotine modulates strategy-based attentional semantic processing in non-smokers. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:389–399
Hong LE, Gu H, Yang Y, Ross TJ, Salmeron BJ, Buchholz B, Thaker GK, Stein EA (2009) Association of nicotine addiction and nicotine’s actions with separate cingulate cortex functional circuits. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:431–441
*Houlihan ME, Pritchard WS, Robinson JH (2001) Effects of smoking/nicotine on performance and event-related potentials during a short-term memory scanning task. Psychopharmacology 156:388–396
Hughes JR (1991) Distinguishing withdrawal relief and direct effects of smoking. Psychopharmacology 104:409–410
Hughes JR (2007) Effects of abstinence from tobacco: valid symptoms and time course. Nicotine Tob Res 9:315–327
*Jacobsen LK, Pugh KR, Menci WE, Gelernter J (2006) C957T polymorphism of the dopamine D2 receptor gene modulates the effect of nicotine on working memory performance and cortical processing efficiency. Psychopharmacology 188:530–540
*Jubelt LE, Barr RS, Goff DC, Logvinenko T, Weiss AP, Evins AE (2008) Effects of transdermal nicotine on episodic memory in non-smokers with and without schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 199:89–98
Kalmijn S, van Boxtel MPJ, Verschuren MWM, Jolles J, Launer LJ (2002) Cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption in relation to cognitive performance in middle age. Am J Epidemiol 156:936–944
*Kelemen WL, Fulton EK (2008) Cigarette abstinence impairs memory and metacognition despite administration of 2 mg nicotine gum. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 16:521–531
Kenney JW, Gould TJ (2008) Modulation of hippocampus-dependent learning and synaptic plasticity by nicotine. Mol Neurobiol 38:101–121
*Kleykamp BA, Jennings JM, Blank MD, Eissenberg T (2005) The effects of nicotine on attention and working memory in never-smokers. Psychol Addict Behav 19:433–438
*Krebs SJ, Petros TV, Beckwith BE (1994) Effects of smoking on memory for prose passages. Physiol Behav 56:723–727
*Kumari V, Gray JA, ffytche DH, Mitterschiffthaler MT, Das M, Zachariah E, Vythelingum GN, Williams SCR, Simmons A, Sharma T (2003) Cognitive effects of nicotine in humans: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 19:1002–1013
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
*Larrison AL, Briand KA, Sereno AB (2004) Nicotine improves antisaccade task performance without affecting prosaccades. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:409–419
*Lawrence NS, Ross TJ, Stein EA (2002) Cognitive mechanisms of nicotine on visual attention. Neuron 36:539–548
*Le Houezec J, Halliday R, Benowitz NL, Callaway E, Naylor H, Herzig K (1994) A low dose of subcutaneous nicotine improves information processing in non-smokers. Psychopharmacology 114:628–634
*Levin ED, Conners CK, Silva D, Hinton SC, Meck WH, March J, Rose JE (1998) Transdermal nicotine effects on attention. Psychopharmacology 140:135–141
Levin ED, McClernon FJ, Rezvani AH (2006) Nicotinic effects on cognitive function: behavioral characterization, pharmacological specification, and anatomic localization. Psychopharmacology 184:523–539
Mansvelder HD, van Aerde AI, Couey JJ, Brussaard AB (2006) Nicotinic modulation of neuronal networks: from receptors to cognition. Psychopharmacology 184:292–305
†Marchant NL, Trawley S, Rusted JM (2008) Prospective memory or prospective attention: physiological and pharmacological support for an attentional model. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:401–411
*McClernon FJ, Gilbert DG, Radtke R (2003) Effects of transdermal nicotine on lateralized identification and memory interference. Hum Psychopharmacol 18:339–343
*Meinke A, Thiel CM, Fink GR (2006) Effects of nicotine on visuo-spatial selective attention as indexed by event-related potentials. Neuroscience 141:201–212
Mitchell SN, Brazell MP, Schugens MM, Gray JA (1990) Nicotine-induced catecholamine synthesis after lesions to the dorsal or ventral noradrenergic bundle. Eur J Pharmacol 179:383–391
†Mumenthaler MS, Taylor JL, O’Hara R, Yesavage JA (1998) Influence of nicotine on simulator flight performance in non-smokers. Psychopharmacology 140:38–41
*Myers CS, Taylor RC, Moolchan ET, Heishman SJ (2008) Dose-related enhancement of mood and cognition in smokers administered nicotine nasal spray. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:588–598
†Neumann DL, Fitzgerald ZT, Furedy JJ, Boyle GJ (2007) Sexually dimorphic effects of acute nicotine administration on arousal and visual-spatial ability in non-smoking human volunteers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86:758–765
Newhouse PA, Potter A, Singh A (2004) Effects of nicotinic stimulation on cognitive performance. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:36–46
Parrott AC (1987) Assessment of psychological performance in applied situations. In: Hindmarch I, Stonier PD (eds) Human psychopharmacology: measures and methods, vol 1. Wiley, Chichester, pp 93–112
Parrott AC, Garnham NJ, Wesnes K, Pincock C (1996) Cigarette smoking and abstinence: comparative effects upon cognitive task performance and mood state over 24 hours. Hum Psychopharmacol 11:391–400
*Perkins KA, Grobe JE, Fonte C, Goettler J, Caggiula AR, Reynolds WA, Stiller RL, Scierka A, Jacob RG (1994) Chronic and acute tolerance to subjective, behavioral and cardiovascular effects of nicotine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:628–638
*Perkins KA, Gerlach D, Broge M, Grobe JE, Sanders M, Fonte C, Vender J, Cherry C, Wilson A (2001) Dissociation of nicotine tolerance from tobacco dependence in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:849–856
*Perkins KA, Lerman C, Coddington SB, Jetton C, Karelitz JL, Scott JA, Wilson AS (2008) Initial nicotine sensitivity in humans as a function of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology 200:529–544
Peters R, Poulter R, Warner J, Beckett N, Burch L, Bulpitt C (2008) Smoking, dementia and cognitive decline in the elderly, a systematic review. BMC Geriatr. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-8-36
*Phillips S, Fox P (1998) An investigation into the effects of nicotine gum on short-term memory. Psychopharmacology 140:429–433
*Poltavski DV, Petros T (2005) Effects of transdermal nicotine on prose memory and attention in smokers and nonsmokers. Physiol Behav 83:833–843
*Poltavski DV, Petros T (2006) Effects of transdermal nicotine on attention in adult non-smokers with and without attentional deficits. Physiol Behav 87:614–624
Poorthuis RB, Goriounova NA, Couey JJ, Mansvelder HD (2009) Nicotinic actions on neuronal networks for cognition: general principles and long-term consequences. Biochem Pharmacol 78:668–676
Posner MI, Rothbart MK (2007) Research on attention networks as a model for the integration of psychological science. Annu Rev Psychol 58:1–23
Richards M, Jarvis MJ, Thompson N, Wadsworth MEJ (2003) Cigarette smoking and cognitive decline in midlife: evidence from a prospective birth cohort study. Am J Public Health 93:994–998
Robinson ML, Houtsmuller EJ, Moolchan ET, Pickworth WB (2000) Placebo cigarettes in smoking research. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:326–332
*Rusted JM, Alvares T (2008) Nicotine effects on retrieval-induced forgetting are not attributable to changes in arousal. Psychopharmacology 196:83–92
†Rusted JM, Trawley S (2006) Comparable effects of nicotine in smokers and nonsmokers on a prospective memory task. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1545–1549
*Rusted J, Graupner L, Warburton D (1995) Effects of post-trial administration of nicotine on human memory: evaluating the conditions for improving memory. Psychopharmacology 119:405–413
*Rusted JM, Graupner L, Tennant A, Warburton DM (1998) Effortful processing is a requirement for nicotine-induced improvements in memory. Psychopharmacology 138:362–368
†Rusted JM, Sawyer R, Jones C, Trawley SL, Marchant NL (2009) Positive effects of nicotine on cognition: the deployment of attention for prospective memory. Psychopharmacology 202:93–102
Sauer J, Wastell DG, Hockey GRJ, Earle F (2003) Performance in a complex multiple-task environment during a laboratory-based simulation of occasional night work. Hum Factors 45:657–669
Sherwood N (1993) Effects of nicotine on human psychomotor performance. Hum Psychopharmacol 8:155–184
†Sherwood N (1995) Effects of cigarette smoking on performance in a simulated driving task. Neuropsychobiology 32:161–165
Snyder FR, Davis FC, Henningfield JE (1989) The tobacco withdrawal syndrome: performance decrements assessed on a computerized test battery. Drug Alc Depend 23:259–266
Streufert S, Pogash R, Piasecki M (1988) Simulation-based assessment of managerial competence: reliability and validity. Personnel Psychol 41:537–557
Sun B, Chen X, Xu L, Sterling C, Tank AW (2004) Chronic nicotine treatment leads to induction of tyrosine hydroxylase in locus coeruleus neurons: the role of transcriptional activation. Mol Pharmacol 66:1011–1021
Swan GE, Lessov-Schlaggar CN (2007) The effects of tobacco smoke and nicotine on cognition and the brain. Neuropsychol Rev 17:259–273
*Thiel CM, Fink GR (2008) Effects of the cholinergic agonist nicotine on reorienting of visual spatial attention and top-down attentional control. Neuroscience 152:381–390
*Thiel CM, Zilles K, Fink GR (2005) Nicotine modulates reorienting of visuospatial attention and neural activity in human parietal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:810–820
Toth E, Sershen H, Hashim A, Vizi ES, Lajtha A (1992) Effect of nicotine on extracellular levels of neurotransmitters assessed by microdialysis in various brain regions: role of glutamic acid. Neurochem Res 17:265–271
*Tucha O, Lange KW (2004) Effects of nicotine chewing gum on a real-life motor task: a kinematic analysis of handwriting movements in smokers and non-smokers. Psychopharmacology 173:49–56
Tulving E (1972) Episodic and semantic memory. In: Tulving E, Donaldson W (eds) Organization of memory. Academic, New York, pp 381–403
U.S. Public Health Service (1964) Smoking and health. Report of the advisory committee to the Surgeon General of the Public Health Service (PHS Publication No. 1103). U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington DC
*Vossel S, Thiel CM, Fink GR (2008) Behavioral and neural effects of nicotine on visuospatial attentional reorienting in non-smoking subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:731–738
*Warburton DM, Skinner A, Martin CD (2001) Improved incidental memory with nicotine after semantic processing, but not after phonological processing. Psychopharmacology 153:258–263
Waters AJ, Sutton SR (2000) Direct and indirect effects of nicotine/smoking on cognition in humans. Addict Behav 25:29–43
West R (1993) Beneficial effects of nicotine: fact or fiction? Addiction 88:589–590
Woolf NJ (1991) Cholinergic systems in mammalian brain and spinal cord. Prog Neurobiol 37:475–524
†Zingler VC, Denecke K, Jahn K, von Meyer L, Krafczyk S, Krams M, Elfont R, Brandt T, Strupp M, Glasauer S (2007) The effect of nicotine on perceptual, ocular motor, postural, and vegetative functions at rest and in motion. J Neurol 254:1689–1697
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and NIH grant T32DA007209-29. We thank Dr. Michael Borenstein for answering questions regarding the conduct of the meta-analyses and Drs. Jack Henningfield and Andrew Waters for comments on the manuscript. We also thank Dr. Rex Robison, Dr. Mary Pfeiffer, Richard Taylor, Heather Andes, Rebecca Evans, and Gina Marrone for assistance in searching, obtaining, and organizing references.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute on Drug Abuse, and NIH grant T32DA007209-29.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heishman, S.J., Kleykamp, B.A. & Singleton, E.G. Meta-analysis of the acute effects of nicotine and smoking on human performance. Psychopharmacology 210, 453–469 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1848-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1848-1