Abstract.
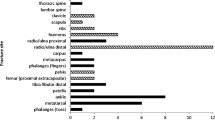
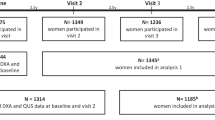
Recent developments in computer-assisted radiographic absorptiometry (RA) and quantitative ultrasound techniques (QUS) provide readily accessible and relatively inexpensive methods for assessing bone mineral status. However, few population-based studies have investigated the ability of RA and ultrasound to predict fracture risk prospectively. We explored the ability of RA and QUS to predict fracture risk among 560 postmenopausal women from the Hawaii Osteoporosis Study; average follow-up was 2.7 years. An incident vertebral fracture was defined as a decrease of more than 15% in vertebral heights on subsequent films. Self-reported nonspine fractures were verified by medical records. The prospective associations of vertebral fractures, nonspine fractures, and any (spine or nonspine) fractures with bone measurements were examined using logistic regression, adjusting for age. Both phalangeal bone mineral density (BMD) and metacarpal BMD, measured using RA, predicted future fracture risk. The age-adjusted odds ratios (corresponding to 1 SD decrease in BMD) for vertebral fractures, nonspine fractures, and any fractures were 3.41, 1.50, and 1.91, respectively, for phalangeal BMD, and 1.71, 1.49, 1.55, respectively for metacarpal BMD. Calcaneal broadband ultrasound attenuation (BUA) also showed significant association with fracture risk, with age-adjusted odds ratios of 1.50, 1.89, and 1.72 for vertebral fractures, nonspine fractures, and any fractures, respectively. We conclude that hand RA and calcaneal BUA are significant predictors of nonspine fracture, vertebral fracture, and overall fracture risk. The attractive features of these techniques, such as portability, relatively low cost, and ease of use, make them promising alternatives to conventional bone measurement techniques used for the assessment of fracture risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 August 1997 / Accepted: 5 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, C., Ross, P., Yates, A. et al. Prediction of Fracture Risk by Radiographic Absorptiometry and Quantitative Ultrasound: A Prospective Study. Calcif Tissue Int 63, 380–384 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900544
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900544