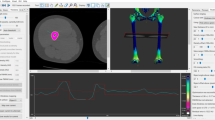
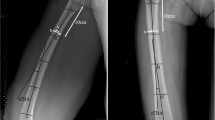
Abstract
Objectives
The goal of this prospective study was to characterize the morphology and physeal changes of the femoral head during maturation using MRI in a population-based group of asymptomatic volunteers.
Materials and methods
Sixty-four pupils (127 hips) of 331 pupils from a primary and high school were asked to take part in this study and were willing to participate. 3T MRI of the hip was obtained at baseline and 1-year follow-up. With these images, we analyzed the femoral morphology and epiphyseal changes related to age, status of the physis, and location on the femur.
Results
The radius of the femoral head and neck increased with age, as expected, (p < 0.001). The epiphyseal extension increased significantly with age (p < 0.05), but epiphyseal tilt and alpha angle showed no differences (p > 0.05). Building groups by using the epiphyseal status, we found that the epiphyseal extension had the highest changes in the "open" group and almost stopped in the "closed" group. The tilt angle did not change significantly (p > 0.05). Significant smaller alpha-angles were found in the "closed" group, however, these were in a normal range in all of them. Correlated to the position, the highest alpha-angle values were located in anterior-superior and superior-anterior position.
Conclusions
Our data can be used as normative values, which can be compared to patients or cohorts with certain risk factors (e.g., professional athletes), this will offer the chance to detect and understand pathological changes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy SB, Ganz R, Müller ME. The prognosis in untreated dysplasia of the hip. A study of radiographic factors that predict the outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(7):985–9.
Goodman DA, Feighan JE, Smith AD, Latimer B, Buly RL, Cooperman DR. Subclinical slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Relationship to osteoarthrosis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(10):1489–97. Erratum in: J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999 Apr;81(4):592. PubMed PMID: 9378734.
Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7):1012–8. PubMed PMID: 15972923.
Ganz R, Leunig M, Leunig-Ganz K, Harris WH. The etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip: an integrated mechanical concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(2):264–72. Epub 2008 Jan 10. Review. PubMed PMID: 18196405; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2505145.
Harris WH. Etiology of osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(213):20–33. PubMed PMID: 3780093.
Murray RO. The aetiology of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. Br J Radiol. 1965;38(455):810–24. PubMed PMID: 5842578.
Stulberg SD, Cordell LD, Harris WH. Unrecognized childhood hip disease: a major cause of idiopathic osteoarthrosis of the hip. The Hip Proceedings of the Third Meeting of The Hip Society. (Ed Amstutz HC). C.V. Mosby Company, Saint Louis 1975;212–28.
Eijer H, Myers SR, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(7):475–81. PubMed PMID: 11602829.
Ito K, Minka 2nd MA, Leunig M, Werlen S, Ganz R. Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect. A MRI-based quantitative anatomical study of the femoralhead-neck offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(2):171–6. PubMed PMID: 11284559.
Siebenrock KA, Wahab KH, Werlen S, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Abnormal extension of the femoral head epiphysis as a cause of cam impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;418:54–60. PubMed PMID: 15043093.
Mamisch TC, Kim YJ, Richolt JA, Millis MB, Kordelle J. Femoral morphology due to impingement influences the range of motion in slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(3):692–8. Epub 2008 Oct 22. PubMed PMID: 18941860; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2635459.
Miese FR, Zilkens C, Holstein A, et al. MRI morphometry, cartilage damage and impaired function in the follow-up after slipped capital femoral epiphysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(6):533–41. Epub 2010 Feb 24. PubMed PMID: 20177672.
Siebenrock KA, Schoeniger R, Ganz R. Anterior femoro-acetabular impingement due to acetabular retroversion. Treatment with periacetabular osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(2):278–86. PubMed PMID: 12571306.
Myers SR, Eijer H, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;363:93–9. PubMed PMID: 10379309.
Eijer H, Berg RP, Haverkamp D, Pécasse GA. Hip deformity in symptomatic adult Perthes' disease. Acta Orthop Belg. 2006;72(6):683–92. PubMed PMID: 17260605.
Kassarjian A, Brisson M, Palmer WE. Femoroacetabular impingement. Eur J Radiol. 2007;63(1):29–35. Epub 2007 May 7. Review. PubMed PMID: 17485190.
Pfirrmann CW, Mengiardi B, Dora C, Kalberer F, Zanetti M, Hodler J. Cam and pincer femoroacetabular impingement: characteristic MR arthrographic findings in 50 patients. Radiology. 2006;240(3):778–85. Epub 2006 Jul 20. Erratum in: Radiology. 2007 Aug;244(2):626. PubMed PMID: 16857978.
Kassarjian A, Belzile E. Femoroacetabular impingement: presentation, diagnosis, and management. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2008;12(2):136–45. Review. PubMed PMID: 18509793.
Jaberi FM, Parvizi J. Hip pain in young adults: femoroacetabular impingement. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7 Suppl 3):37–42. Review. PubMed PMID: 17919591.
Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J. The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(4):556–60. PubMed PMID: 12043778.
Ganz R, Parvizi J, Beck M, Leunig M, Nötzli H, Siebenrock KA. Femoroacetabular impingement: a cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(417):112–20. Review. PubMed PMID: 14646708.
Locher S, Werlen S, Leunig M, Ganz R. [MR-Arthrography with radial sequences for visualization of early hip pathology not visible on plain radiographs]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2002;140(1):52–7. German. PubMed PMID: 11898065.
Werlen S, Leunig M, Ganz R. Magnetic resonance arthrography of the hip in femoroacetabular impingement: technique and findings operative techniques in orthopaedics. 2005;15(3):191–203.
Eijer H, Leunig M, Mahomed MN, Ganz R. Cross-table lateral radiograph for screening of anterior femoral head-neck offset in patients with femoro-acetabular impingement. Hip Int. 2001;11:37–41.
Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabulum and congenital subluxation of the hip joint with special reference to the complication of osteoarthritis. JAMA. 1940;115(1):81. doi:10.1001/jama.1940.02810270083038.
Herndon CH, Heyman CH. Legg-Perthes disease; a method for the measurement of the roentgenographic result. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1950;32(A:4):767–78. PubMed PMID: 14784485.
Steppacher SD, Tannast M, Werlen S, Siebenrock KA. Femoral morphology differs between deficient and excessive acetabular coverage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(4):782–90. Epub 2008 Feb 21. PubMed PMID: 18288550; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2504673.
Sasaki T, Ishibashi Y, Okamura Y, Toh S, Sasaki T. MRI evaluation of growth plate closure rate and pattern in the normal knee joint. J Knee Surg. 2002;15(2):72–6. PubMed PMID: 12013076.
Ecklund K, Jaramillo D. Patterns of premature physeal arrest: MR imaging of 111 children. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(4):967–72. PubMed PMID: 11906884.
Craig JG, Cody DD, Van Holsbeeck M. The distal femoral and proximal tibial growth plates: MR imaging, three-dimensional modeling and estimation of area and volume. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(6):337–44. Epub 2004 Apr 3. PubMed PMID: 15064874.
Dvorak J, George J, Junge A, Hodler J. Age determination by magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in adolescent male football players. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41(1):45–52. Epub 2006 Oct 4. PubMed PMID: 17021001; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2465138.
Ulrich Welsch, Sobotta Lehrbuch Histologie: Zytologie, Histologie, Mikroskopische Anatomie.Seite 142–146 Verlag: Urban & Fischer Verlag; Auflage: 2., völlig überarb. A. (21. August 2006) Sprache: Deutsch ISBN-10: 3437444301.
Tanzer M, Noiseux N. Osseous abnormalities and early osteoarthritis: the role of hip impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(429):170–7. Review. PubMed PMID: 15577483.
Southwick WO. Osteotomy through the lesser trochanter for slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967;49(5):807–35. PubMed PMID: 6029256.
Strout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass Correlations: Uses in Assessing Rater Reliability. Psychology Bulletin. 1979;86:420–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kienle, KP., Keck, J., Werlen, S. et al. Femoral morphology and epiphyseal growth plate changes of the hip during maturation: MR assessments in a 1-year follow-up on a cross-sectional asymptomatic cohort in the age range of 9–17 years. Skeletal Radiol 41, 1381–1390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1358-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1358-9