Abstract
Purpose
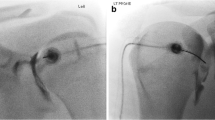
Intra-articular glenohumeral injections have an important role for therapeutic benefit and diagnostic information. Therefore, it is very important that the injected material should reach its desired target. This study assessed the accuracy of an anterior intra-articular injection in fresh cadavers.
Methods
A total of 50 shoulders of 25 fresh cadavers were included in the study. Anterior placement of a spinal needle using a location just 1 cm lateral to the coracoid, without radiographic assistance were performed. After the needle was placed and estimated to be intra-articular 1 cc of acrylic dye was injected into the joint to determine accuracy of position.
Results
Ninety-six percent of injections were accurately administered into the glenohumeral joint and 4% in the surrounding soft tissues and capsule.
Conclusion
Based on our cadaveric study, an unassisted anterior injection to the glenohumeral joint could be accurately placed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebajo AO, Nash P, Hazleman BL (1990) A prospective double blind dummy palcebo controlled study comparing triamcinolone hexacetonide injection with oral diclofenac 50 mg TDS in patients with rotator cuff tendinitis. J Rheumatol 17:1207–1210
Chung CB, Dwek JR, Feng S, Resnick D (2001) MR arthrography of the glenohumeral joint: a tailored approach. AJR 177:217–219
Dacre JE, Beeney N, Scott DL (1989) Injections and physiotherapy for he painfull stiff shoulder. Ann Rheum Dis 48:322–325. doi:10.1136/ard.48.4.322
Eustace JA, Brophy DP, Gibney RP, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O (1997) Comparison of the accuracy of steroid placement with clinical outcome in patients with shoulder symptoms. Ann Rheum Dis 56:59–63
Farmer KD, Hughes PM (2002) MR Arthrograph of the shoulder: fluoroscopically guided technique using a posterior approach. AJR 178:433–434
Ford LT, DeBender J (1979) Tendon rupture after local steroid injection. South Med J 72:827–830
Hancharad N, Shanahan D, Howe T, Thompson J, Goodchild L (2006) Accuracy and dispersal of subacromial and glenohumeral injections in cadavers. J Rheumatol 33:1143–1146
Hulstyn MJ, Fadale PD (1995) Arthroscopic anatomy of the shoulder. Orthop Clin North Am 26:597–612
Jones A, Regan M, Ledingham J, Patrick M, Mahire A, Dohery M (1993) Importance of intraarticular steroid injections. BMJ 307:1329–1330
Kerlan RK, Glousman RE (1989) Injections and techniques in athletic medicine. Clin Sports Med 8:541–560
Naredo E, Cabero F, Beneyto P, Cruz A, Mondejar B, Uson J, Palop MJ, Crespo M (2004) A randomized comparative study of short term response to blind injection versus sonographic guided injection of local corticosteroids in patients with painful shoulder. J Rheumatol 31:308–314
Nevasier RJ (1983) Painful conditions affecting the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:63–69
Neustadt DH (1991) Local corticosteroid injection therapy in soft tissue rheumatic conditions of the hand and wrist. Arthritis Rheum 34:923–926. doi:10.1002/art.1780340721
Partington PF, Broome GH (1998) Diagnostic injection around the shoulder: hit and miss? A cadaveric study of injection accuracy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 7:147–150. doi:10.1016/S1058-2746(98)90226-9
Petri M, Dobrow R, Neiman R, Whiting O’Keefe Q, Seaman WE (1987) Randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study of treatment of the painful shoulder. Arthritis Rheum 30:1040–1045. doi:10.1002/art.1780300911
Sethi PM, Kingston S, Elattrache N (2005) Accuracy of anterior intraarticular injection of the glenohumeral joint. Arthroscopy 21:77–80. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2004.09.009
Tallia A, Cardone DA (2003) Diagnostic and therapeutic injection of the shoulder region. Am Fam Physician 67:1271–1278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esenyel, C.Z., Ozturk, K., Demirhan, M. et al. Accuracy of anterior glenohumeral injections: a cadaver study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130, 297–300 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0811-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-008-0811-7