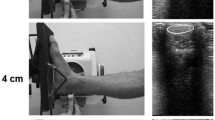
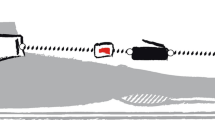
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to investigate the time course of changes in human tendon properties and metabolism during resistance training and detraining. Nine men (21–27 years) completed 3 months of isometric plantar flexion training and another 3 months of detraining. At the beginning and on every 1 month of training and detraining periods, the stiffness, blood circulation (blood volume and oxygen saturation), serum procollagen type 1 C-peptide (P1P; reflects synthesis of type 1 collagen), echointensity (reflects collagen content), and MRI signal intensity (reflects collagen structure) of the Achilles tendon were measured. Tendon stiffness did not change until 2 months of training, and the increase (50.3%) reached statistical significance at the end of the training period. After 1 month of detraining, tendon stiffness had already decreased to pre-training level. Blood circulation in the tendon did not change during the experimental period. P1P increased significantly after 2 months of training. Echointensity increased significantly by 9.1% after 2 months of training, and remained high throughout the experiment. MRI signal intensity increased by 24.2% after 2 months and by 21.4% after 3 months of training, but decreased to the pre-training level during the detraining period. These results suggested that the collagen synthesis, content, and structure of human tendons changed at the 2-month point of training period. During detraining, the sudden decrease in tendon stiffness might be related to changes in the structure of collagen fibers within the tendon.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arampatzis A, Karamanidis K, Albracht K (2007) Adaptational responses of the human Achilles tendon by modulation of the applied cyclic strain magnitude. J Exp Biol 210:2743–2753
Boushel R, Langberg H, Green S, Skovgaard D, Bulow J, Kjaer M (2000) Blood flow and oxygenation in peritendinous tissue and calf muscle during dynamic exercise in humans. J Physiol 524:305–313
Burgess KE, Connick MJ, Graham-Smith P, Pearson SJ (2007) Plyometric vs. isometric training influences on tendon properties and muscle output. J Strength Cond Res 21:986–989
Carroll CC, Dickinson JM, Haus JM, Lee GA, Hollon CJ, Aagaard P, Magnusson SP, Trappe TA (2008) Influence of aging on the in vivo properties of human patellar tendon. J Appl Physiol 105:1907–1915
Carroll CC, Dickinson JM, LeMoine JK, Haus JM, Weinheimer EM, Hollon CJ, Aagaard P, Magnusson SP, Trappe TA (2011) Influence of acetaminophen and ibuprofen on in vivo patellar tendon adaptations to knee extensor resistance exercise in older adults. J Appl Physiol (in press)
de Boer MD, Maganaris CN, Seynnes OR, Rennie MJ, Narici MV (2007) Time course of muscular, neural and tendinous adaptations to 23 day unilateral lower-limb suspension in young men. J Physiol 583:1079–1091
Du J, Pak BC, Znamirowski R, Statum S, Takahashi A, Chung C, Bydder GM (2009) Magic angle effect in magnetic resonance imaging of the Achilles tendon and enthesis. Mag Reson Imag 27:557–564
Erickson SJ, Prost RW, Timins ME (1993) The “magic angle” effect: background physics and clinical relevance. Radiology 188:23–25
Greive DW, Pheasant S, Cavagna, PR (1978) Prediction of gastrocnemius length from knee and ankle joint posture. In: Asmussen E, Jorgensen K (eds) Biomechanics VI-A, International series in biomechanics. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 405–412
Garnero P, Delmas PD (1993) Assessment of the serum levels of bone alkaline phosphatase with a new immunoradiometric assay in patients with metabolic bone disease. J Clil Endocrinol Met 77:1046–1053
Jackson BF, Smith RKW, Price JS (2003) A molecular markers of type 1 collagen metabolism reflects changes in connective tissue remodeling associated with injury to the equine superficial digital flexor tendon. Equine Ver J 35:211–213
Kashima S (2003) Spectroscopic measurement of blood volume and its oxygenation in a small volume of tissue using red laser lights and differential calculation between two point detections. Optics Laser Technol 35:485–489
Klein MB, Pham H, Yalamanchi N, Chang J (2001) Flexor tendon wound healing in vitro: the effects of lactate on tendon cell proliferation and collagen production. J Hand Surg 26:847–854
Kongsgaard M, Kovanen V, Aagaard P, Doessing S, Hansen P, Laursen AH, Kaldau NC, Kjaer M, Magnusson SP (2009) Corticosteroid injections, eccentric decline squat training and heavy slow resistance training in patellar tendinopathy. Scand J Med Sci Sports 19:790–802
Kubo K, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T (1999) Influence of elastic properties of tendon structures on jump performance in humans. J Appl Physiol 87:2090–2096
Kubo K, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2002) Effects of resistance and stretching training programs on the viscoelastic properties of tendon structures in vivo. J Physiol 538:219–226
Kubo K, Akima H, Ushiyama J, Tabata I, Fukuoka H, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2004) Effects of resistance training during bed rest on the viscoelastic properties of tendon structures in lower limb. Scand J Med Sci Sports 14:296–302
Kubo K, Morimoto M, Komuro T, Yata H, Tsunoda N, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2007) Effects of plyometric and weight training on muscle-tendon complex and jump performance. Med Sci Sports Exer 39:1801–1810
Kubo K, Ikebukuro T, Tsunoda N, Kanehisa H (2008a) Changes in oxygen consumption of human muscle and tendon following repeat muscle contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:859–866
Kubo K, Ikebukuro T, Tsunoda N, Kanehisa H (2008b) Noninvasive measures of blood volume and oxygen saturation of human Achilles tendon by red laser lights. Acta Physiol 193:257–264
Kubo K, Ikebukuro T, Yaeshima K, Kanehisa H (2009a) Effects of different duration contractions on elasticity, blood volume, and oxygen saturation of human tendon in vivo. Eur J Appl Physiol 106:445–455
Kubo K, Ikebukuro T, Yaeshima K, Yata H, Tsunoda N, Kanehisa H (2009b) Effects of static and dynamic training on the stiffness and blood volume of tendon in vivo. J Appl Physiol 106:412–417
Kubo K, Ikebukuro T, Yata H, Tsunoda N, Kanehisa H (2010) Time course of changes in muscle and tendon properties during strength training and detraining. J Strength Cond Res 24:322–331
Kubo K, Yuki K, Ikebukuro T (2011) Changes in bone alkaline phosphatase and procollagen type-1 C-peptide after static and dynamic exercises. Res Quart Exer Sport (in press)
Langberg H, Skovgaard D, Karamouzis M, Bulow J, Kjaer M (1999) Metabolism and inflammatory mediators in the peritendinous space measured by microdialysis during intermittent isometric exercise in humans. J Physiol 515:919–927
Langberg H, Skovgaard D, Asp S, Kjaer M (2000) Time pattern of exercise-induced changes in type 1 collagen turnover after prolonged endurance exercise in humans. Calcif Tissue Int 67:41–44
Langberg H, Rosendal L, Kjaer M (2001) Training-induced changes in peritendinous type 1 collagen turnover determined by microdialysis in humans. J Physiol 534:297–302
Magnusson SP, Aagaard P, Rosager S, Poulsen PD, Kjaer M (2001) Load-displacement properties of the human triceps surae aponeurosis in vivo. J Physiol 531:277–288
Maimoun L, Manetta J, Couret I, Dupuy AM, Mariano-Goulart D, Micallef JP, Peruchon E, Rossi M (2006) The intensity level of physical exercise and the bone metabolism response. Int J Sports Med 27:105–111
Miller BF, Olesen JL, Hansen M, Dossing S, Crameri RM, Welling RJ, Langeberg H, Flyvbjerg A, Kjaer M, Babraj JA, Smith K, Rennie MJ (2005) Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise. J Physiol 567:1021–1033
Nagy A, Dyson S (2011) Anatomical, magnetic resonance imaging and histological findings in the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon of forelimbs in nonlame horses. Equine Ver J 43:309–316
Nieminen MT, Rieppo J, Toyras J, Hakumaki JM, Silvennoinen J, Hyttinen MM, Helminen HJ, Jurvelin JS (2001) T2 relaxation reveals spatial collagen architecture in articular cartilage: a comparative quantitative MRI and polarized light microscopic study. Mag Reson Med 46:487–493
Nosaka K, Clarkson PM (1996) Changes in indicators of inflammation after eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Med Sci Sports Exer 28:953–961
Reimers CD, Fleckenstein JL, Witt TN, Muller-Felber W, Pongratz DE (1993a) Muscular ultrasound in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies of adults. J Neurol Sci 116:82–92
Reimers K, Reimers CD, Wagner S, Paetzke I, Pongratz DE (1993b) Skeletal muscle sonography. A correlative study of echogenicity and morphology. J Ultrasound Med 12:73–77
Risteli L, Risteli J (1993) Biochemical markers of bone metabolism. Ann Med 25:385–393
Shalabi A, Kristoffersen-Wiberg M, Papadogiannakis N, Aspelin P, Movin T (2002) Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and histopathology in chronic Achilles tendinosis. A longitudinal MR study of 15 patients. Acta Radiol 43:198–206
Soyama N, Kuratsu J, Ushio Y (1995) Correlation between magnetic resonance images and histology in meningiomas: T2-weighted images indicate collagen contents in tissue. Neurol Med Chir 35:438–441
van Holsbeeck M, Introcaso JH (1992) Musculoskeletal ultrasonography. Radiol Clin Am 30:907–925
Virtanen P, Viitasalo JT, Vuori J, Vaananen K, Takala TES (1993) Effect of concentric exercise on serum muscle and collagen markers. J Appl Physiol 75:1272–1277
Yalamanchi N, Klein MB, Pham HM, Longaker MT, Chang J (2004) Flexor tendon wound healing in vitro: lactate up-regulation of TGF-ß expression and functional activity. Plastic Reconstr Surg 113:625–632
Yoon JH, Halper J (2005) Tendon proteoglycans: biochemistry and function. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 5:22–34
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (A) (21680047 to K. Kubo) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and Yamaha Motor Foundation for Sports. The authors thank the staff of Kouikai Clinic for their technical assistance with MRI measurements. The authors also thank Mr. Yuki K and Mr. Sato H (Kishimoto Clinical Laboratory Group) for their conscientious work on the analyses of serum biochemical markers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Toshio Moritani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, K., Ikebukuro, T., Maki, A. et al. Time course of changes in the human Achilles tendon properties and metabolism during training and detraining in vivo. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 2679–2691 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2248-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2248-x