Abstract
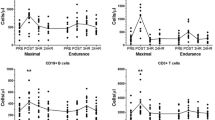
This study was designed to examine immunological responses to an acute bout of cycle ergometry exercise before and after moderate endurance training. Previously sedentary males were randomly assigned to matched training (n=9) or control (n=6) groups. Training comprised 12 weeks during which supervised cycle ergometer exercise took place [30 min at 65–70% of maximal oxygen intake\((\dot VO_{2max} )\), 4–5 days · week−1]. An acute bout of exercise (60 min; 60%\(\dot VO_{2max} \) was performed initially and after the 12-week interval. Samples of peripheral venous blood were taken at rest, after 30 and 60 min of exercise, and at 30 and 120 min post-exercise. Training improved\(\dot VO_{2max} \) by an average of 20% (40.6 to 49.2 ml · kg−1 · min−1). Relative to baseline and control measures, the resting concentration of (CD3-CD16+/CD56+) natural killer (NK) cells increased by 22% (P<0.05). The resting count of total CD25+ [interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) α chain] lymphocytes did not change following training, but dual staining analysis showed a 100% increase in the fraction of CD16+ CD25+ NK cells (P < 0.05). Likewise the resting CD122+ (IL-2Rβ chain) lymphocyte count increased 35% after training, the greatest increases (44%) being in CD16+ CD122+ NK cells (P<0.05). Soluble IL-2R levels also increased 33% (P< 0.05) after training. Following acute exercise at the same relative intensity; trained individuals exhibited a larger increase in the NK cell count, reduced lymphocytopenia, and attenuation of exercise-induced suppression of lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2 production (P<0.05). In addition, smaller increases in CD4 and CD8 counts during exercise were noted, but with faster recovery post-exercise (P<0.05). Addition of recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2) to phytohemagglutinin-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures did not reverse exercise-induced suppression of cell proliferation, either before or after training. However, rIL-2 did augment the spontaneous blastogenesis of exercise and post-training samples relative to baseline (P < 0.05). We conclude that moderate endurance training is associated with sustained alterations in immune function, both at rest and when exercising. Further investigations are necessary to determine the impact on overall health and susceptibility to disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baj A, Kantorski J, Majewska E, Zeman K, Pokoca L, Fornalczyk E, Tchorzewsk, H, Sulowska Z, Lewicki R (1994) Immunological status of competitive cyclists before and after the training season. Int J Sports Med 15:319–324
Baum M, Liesen H, Enneper J (1994) Leukocytes, lymphocytes, activation and cell adhesion molecules in middle-distance runners under different conditions. Int J Sports Med 15: S122-S126
Benschop RJ, Oostveen FG, Heijnen CJ, Ballieux RE (1993)β 2-Adrenergic stimulation causes detachment of natural killer cells from cultured endothelium. Eur J Immunol 23:3242–3247
Brahmi Z, Thomas JE, Park M, Dowdeswell IRG (1985) The effect of acute exercise on natural killer cell activity of trained and sedentary human subjects. J Clin Immunol 5:321–328
Crary B, Borysenko M, Sutherland DC, Kutz I, Borysenko JZ, Benson H (1983) Decrease in mitogen responsiveness of mononuclear cells from peripheral blood after epinephrine administration in humans. J Immunol 130:694–6971
Crist DM, Mackinnon LT, Thompson RF, Atterbom HA, Egan PA (1989) Physical exercise increases natural cellular-mediated tumor cytotoxicity in elderly women. Gerontology 35:66–71
Dhabhar FS, Miller AH, McEven BS, Spencer RL (1995) Effects of stress on immune cell distribution. Dynamics and hormonal mechanisms. J Immunol 154:5511–5527
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma and reds cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Drummer R, Possechert G, Nestle F, Witzgall R, Burger M, Becker JC, Schäfer E, Wiede J, Sebald W, Berg G (1992) Soluble interleukin-2 receptors inhibit interleukin-2 dependent proliferation and cytotoxicity: explanation for diminished natural killer cell activity in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 98:50–54
Dufaux B, Order U (1989) Plasma elastase-alpha-l-antitrypsin, tumor necrosis factor and soluble interleukin-2 receptor after prolonged exercise. Int J Sports Med 10:434–438
Espersen GT, Elbaek A, Ernst E, Toft E, Kaalund S, Jersild C, Grunnet N (1990) Effect of physical exercise on cytokines and lymphocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 98:395–400
Feldman R, Hunninghake GW, McArdle A (1987) β-Adrenergic receptor-mediated suppression of interleukin-2 receptors in human lymphocytes. J Immunol 139:3355–3359
Ferry A, Pichard F, Duvallet A, Weill B, Rieu M (1990) Changes in blood leukocyte populations induced by acute maximal and chronic submaximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 59:435–442
Frey MJ, Mancini D, Fischberg D, Wilson JR, Molinoff PB (1989) Effect of exercise duration on density and coupling of betaadrenergic receptors on human mononuclear cells. J Appl Physiol 66:1494–1500
Fry RW, Morton AR, Keast D (1992) Acute intensive interval training and T lymphocyte function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:339–345
Gannon GA, Shek PN, Shephard RJ (1995) Natural killer cells: modulation by intensity and duration of exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev 1:26–48
Gimenez M, Mohan-Kumar T, Humbert JC, DeTalance N, Teboul M, Belenguer FJ (1987) Training and leukocyte, lymphocyte and platelet response to dynamic exercise. J Sports Med 27:172–177
Gleeson M, McDonald WA, Cripps AW, Pyne DB, Clancy RL, Fricker PA (1995) The effect on immunity of long-term intensive training in elite swimmers. Clin Exp Immunol 102:210–216
Gmünder FK, Joller PW, Joller-Jemelka HI, Bechler B, Cogoli M, Ziegler WH, Müller J, Aeppli RE, Cogoli A (1990) Effect of herbal yeast food and long distance running on immunological parameters. Br J Sports Med 24:103–112
Gray AB, Smart YC, Telford RD, Weidmann MJ, Roberts TK (1992) Anaerobic exercise causes transient changes in leukocyte subsets and IL-2R expression. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:1332–1338
Haahr PM, Pederson BK, Fomsgaard A, Tvede N, Diamant M, Klarlund K, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Bendtzen K (1991) Effect of physical exercise on in vitro production of IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-2 and IFN-γ. Int J Sports Med 12:223–227
Hoffman-Goetz L, Sweeny AL (1994) Lymphokine activated killer cell activity following voluntary physical activity in mice. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 34:83–90
Iverson P, Stockland A, Rosland B, Benestad HB (1994) Adrenaline-induced leukocytosis: recruitment of blood cells from rat spleen, bone marrow and lymphatics. Eur J Appl Physiol 68:219–227
Janssen GME, van Wersch JWJ, Kaiser V, Does RJMM (1989) White cell system changes associated with a training period of 18-20 months: a transverse and a longitudinal approach. Int J Sports Med 10:5176-S180
Kahn MM, Sansoni P, Silverman ED, Melmon KL (1986)β-Andrenergic receptors on human suppressor, helper, and cytolytic lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 35:1137–1142
Landmann RMA (1992) Beta-adrenergic receptors in human leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Clin Invest 22:30–36
LaPerriere A, Antoni MH, Ironson G, Perry A, McCabe P, Klimas N, Helder L, Schneiderman N, Fletcher MA (1994) Effects of aerobic exercise training on lymphocyte subpopulations. Int J Sports Med 15:S127-S130
Lewicki R, Tchorzewski H, Majewska E, Nowak Z, Baj Z (1988) Effect of maximal physical exercise on T-lymphocyte subpopulations and on IL-1 and IL-2 production in vitro. Int J Sports Med 9:114–117
Lin Y, Jan M, Tsai T, Chen H (1995) Immunomodulatory effects of acute exercise bout in sedentary and trained rats. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:73–78
MacNeil R, Hoeffman-Goetz L (1993) Chronic exercise enhances in vivo and in vitro cytotoxic mechanisms of natural immunity in mice. J Appl Physiol 74:338–395
Maisel AS, Harris T, Rearden CA, Michel MC (1990)β-Andrenergic receptors in lymphocyte subsets after exercise. Circulation 83:2003–2010
Mitchell JB, Paquet AJ, Pizza FX, Starling RD, Holtz RW, Grandjean PW (1993) Effect of aerobic training on immune function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:S78
Ndon JA, Snyder AC, Foster C, Wehrenberg WB (1992) Effects of chronic intense exercise training on the leukocyte response to acute exercise. Int J Sports Med 13:176–182
Nehlsen-Cannarella SL, Nieman DC, Balk-Lamberton AJ, Markoff PA, Critton DBW, Gusewitch G, Lee JW (1991) The effects of moderate exercise training on the immune response. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:64–70
Nieman DC, Miller AR, Henson DA, Warren BJ, Gusewitch G, Johnson RL, Davis JM, Butterworth DE, Herring JL, Nehlsen-Cannarella SL (1994) Effect of high-versus moderate-intensity exercise on lymphocyte subpopulations and proliferative responses. Int J Sports Med 15:199–206
Nieman DC, Brendle D, Henson DA, Suttles J, Cook VD, Warren BJ, Butterworth DE, Fagoaga OR, Nehlsen-Cannarella SL (1995) Immune function in athletes versus nonathletes. Int J Sports Med 16:329–333
Oshida Y, Yamanouchi K, Hayamizu S, Sato Y (1988) Effect of acute physical exercise on lymphocyte subpopulations in trained and untrained subjects. Int J Sports Med 9:137–140
Pedersen BK, Tevde N, Christensen LD, Klarlund K, Kragbak S, Halkjaer-Kristensen J (1989) Natural killer cell activity in peripheral blood of highly trained and untrained persons. Int J Sports Med 10:129–131
Peters C, Lötzerich H, Niemeier B, Schüle K, Uhlenbruck G (1994) Influence of moderate exercise training on natural killer cytotoxicity and personality traits in cancer patients. Anticancer Res 14:1033–1036
Pizza FX, Flynn MG, Sawyer T, Brolinson PG, Starling RD, Andres FF (1995) Run training versus cross-training: effect of increased training on circulating leukocyte subsets. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27:355–362
Rhind SG, Shek PN, Shinkai S, Shephard RJ (1994) Differential expression of interleukin-2 receptor alpha (p55) and beta (p70-75) chains in relation to natural killer cell subsets and aerobic fitness. Int J Sports Med 15:311–318
Rhind SG, Shek PN, Shephard RJ (1995) The impact of exercise on cytokines and receptor expression. Exerc Immunol Rev 1:97–148
Rose-John S, Heinrich PC (1994) Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: generation and biological function. Biochem J 300:281–290
Rubin LA, Nelson DL (1990) The soluble IL-2 receptor — biology, function and clinical application. Ann Intern Med 113:619–627
Schedlowski M, Roland J, Stratmann G, Richter S, Hadicke Tewes U, Wagner TOF, Schmidt RE (1993) Changes of natural killer cells during acute psychological stress. J Clin Immunol 13:119–126
Semenzato G, Zambello R, Pizzolo G (1992) Interleukin-2 receptor expression in health and disease. In Waxman J, Balkwill F (eds) Interleukin-2. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 78–105
Shectman O, Elizondo R, Taylor M (1988) Exercise augments interleukin-2 induction. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20: S18
Shek PN, Sabiston BH, Buguet A, Radomski MW (1995) Strenuous exercise and immunological changes. A multiple-timepoint analysis of leukocyte subsets, CD4/CD8 ratio, immunoglobulin production and NK cell response. Int J Sports Med 16:466–474
Shinkai S, Shore S, Shek PN, Shephard RJ (1992) Acute exercise and immune function. Int J Sports Med 13:542–461
Simpson RJ, Hoffman-Goetz L (1990) Exercise stress an. murine natural killer cell function. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 195:129–135
Smith J, Chi D, Salzar S, Krish G, Berk S, Reynolds S, Cameron G (1993) Effect of moderate exercise on proliferative responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 33:152–158
Sprenger H, Jacobs C, Nain M, Gressner AM, Prinz H, Wesemann W, Gemsa D (1992) Enhanced release of cytokines, interleukin-2 receptors, and neopterin after long distance running. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 63:188–195
Stallone DD (1994) The influence of obesity and its treatment on the immune system. Nutr Rev 52:37–50
Tharp GD, Preuss TL (1991) Mitogenic response of T-lymphocytes to exercise training and stress. J Appl Physiol 70:2535–2538
Thomson SP, McMahon LJ, Nugent CA (1980) Endogenous cortisol: a regulator of the number of lymphocyes in peripheral blood. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 17:506–514
Tilz GP, Dome W, Diez-Ruiz A, Weiss G, Brezinschek R, Brezinschek HP, Huttl E, Wachter H, Fuchs D (1993) Increased immune activation during and after physical exercise. Immunobiology 188:194–202
Tits LJ van, Michel MC, Grosse-Wilde H, Happel M, Eigler F-W, Sliman A, Brodde O-E (1990) Catecholamines increase lymphocyteβ 2-adrenergic receptors via aβ 2-adrenergic, spleendependent process. J Appl Physiol 258: E191-E202
Tvede N, Kappel M, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Galbø H, Pedersen BK (1993) The effect of light, moderate and severe bicycle exercise on lymphocyte subsets, natural and lymphokine activated killer cells, lymphocyte proliferative response and interleukin-2 production. Int J Sports Med 14:275–282
Tvede N, Kappel M, Klarlund K, Duhn S, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Kjaer M, Galbo H, Pedersen BK (1994) Evidence that the effect of bicyle exercise on blood mononuclear cell proliferative responses and subsets is mediated by epinephrine. Int J Sports Med 15:100–104
Verde TJ, Thomas S, Shek P, Shephard RJ (1992) Responses of lymphocyte subsets, mitogen-stimulated cell proliferation, and immunoglobulin synthesis to vigorous exercise in well-trained athletes. Clin J Sport Med 2:87–92
Watson RS, Moriguchi S, Jackson JC, Werner L, Wilmore JH, Freund BJ (1986) Modification of cellular immune function in humans by endurance exercise training duringβ-adrenergic blockade with atenolol or propranolol. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:95–100
Weiss C, Kinscherf R, Roth S, Friedmann B, Fischbach T, Reus J, Dröge W, Bärtsch P (1995) Lymphocyte subpopulations and concentrations of soluble CD8 and CD4 antigen after anaerobic training. Int J Sports Med 16:16–19
Westermann J, Pabst R (1992) Distribution of lymphocyte subsets and natural killer cells in the human body. Clin Invest 70:539–554
Zola H (1994) Detection of receptors for cytokines and growth factors. Immunologist 2:47–50
Zorn U, Dallmann I, Grobe J, Kirchner H, Poliwoda H, Atzpodien J (1994) Soluble interleukin 2 receptors abrogate IL-2 induced activation of peripheral mononuclear cells. Cytokine 6:358–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhind, S.G., Shek, P.N., Shinkai, S. et al. Effects of moderate endurance exercise and training on in vitro lymphocyte proliferation, interleukin-2 (IL-2) production, and IL-2 receptor expression. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 74, 348–360 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02226932
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02226932