Abstract
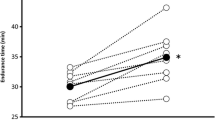
The present study used untrained subjects to examine the effect of acute hypobaric exposure during endurance training on subsequent exercise performance at sea level. Two groups, each of nine subjects, completed 5 weeks of endurance training [cycle ergometer exercise for 45 min, three times per week at a heart rate corresponding to 70% of that achieved at the maximal O2 consumption (V˙O2 max ) either at sea level or at high altitude] in a hypobaric chamber, under either normobaric [sea level, SL; 750 mmHg (100 kPa) ≈90 m] or hypobaric [altitude, ALT; 554 mmHg (73.4 kPa) ≈ 2500 m] conditions and the changes in SL V˙O2 max , SL endurance time and peak blood lactate during the endurance test compared. While each group showed increases in both SL V˙O2 max (≈12%) and SL endurance time (≈71%), there were no significant differences between the groups [SL V˙O2 max , mean (SE) – SL group: pre-training = 42.4 (3.5), post-training = 46.1 (3.5) ml · kg−1· min−1, P < 0.005; ALT group: pre-training = 40.8 (2.6), post-training = 47.2 (3.4) ml · kg−1· min−1, P < 0.01; SL endurance time – SL group: pre-training 7.1 (1.5), post-training 11.8 (2.9) min, P < 0.01; ALT group: pre-training = 7.5 (0.6), post-training = 13.3 (1.4) min, P < 0.001]. Peak blood lactate during the endurance test was not altered by either training regimen. It is concluded that acute exposure of untrained subjects to hypobaric hypoxia during endurance training has no synergistic effect on the degree of improvement in either SL V˙O2 max or endurance time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 3 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emonson, D., Aminuddin, A., Wight, R. et al. Training-induced increases in sea level V˙O2 m a x and endurance are not enhanced by acute hypobaric exposure. Eur J Appl Physiol 76, 8–12 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050206
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050206