Summary
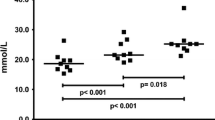
Fifteen men were studied during 100 m, 400 m and 3,000 m runs at maximal speed to determine total urinary protein and albumin excretion rates in relation to different distances of running. Venous blood lactate rose to 7.5 mmol · l−1 after the 100 m and 3,000 m events, while reaching 12 mmol · l−1 after the 400 m dash. Total urinary protein excretion increased to 330, 1640 and 565 μg · min−1 after the 100 m, 400 m and 3,000 m runs respectively, as compared with basal values (70 μg · min−1). In the meantime, albumin excretion increased respectively by 5, 25 and 18 fold of the resting values. The renal clearance of albumin increased to 0.84, 5.62 and 3.35 μl · min−1 after the three runs, as compared with a mean value of 0.19 μl · min−1 at rest. Exponential relationships (r=0.85) were recorded between post-exercise venous lactate and albumin, and total protein excretion. The present work illustrates the major influence of the intensity of exercise (anaerobic glycolytic component), rather than its duration, on the excretion rate of urinary proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantone A, Cerretelli P (1960) Effect of training on proteinuria following muscular exercise. Int Z Angew Physiol Arbeitsphysiol 18:324–329
Delforge E, Delforge B, Poortmans JR (1969) Influence of increasing activity on the protein level in serum, urine and sweat. Med Sport 3:353–355
Doumas BT, Watson WA, Briggs HG (1971) Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta 31:87–96
Everall PH, Wright GH (1958) Low pressure ultrafiltration of protein containing fluids. J Med Lab Technol 15:209–213
Govaerts A, Delanne R (1940) Influence de l'intensité du travail musculaire sur la diurèse, l'albuminurie et la cylindurie. Bruxelles méd 20:361–369
Gutmann I, Wahlefeld AW (1974) L(+) Lactate. Determination with lactate dehydrogenase and NAD. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 1464–1468
Hellebrandt FA, Bragdon E, Kelso LEA (1932) Studies on albuminuria following exercise. II Its relationship to the speed of doing work. Am J Physiol 101:365–375
Heremans JF (1958) La réaction de Donaggio. Ses fondements biochimiques et ses applications en pathologie. Rev Belge Pathol Med Exptl 26:264
Javitt NB, Miller AT (1952) Mechanism of exercise proteinuria. J Appl Physiol 4:834–839
Kachadorian WA, Johnson RE (1970) Renal responses to various rates of exercise. J Appl Physiol 28:748–752
Mancini G, Carbonara AO, Heremans JF (1965) Immunochemical quantifications of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry 2:225–254
Mark DD, Zimmer A (1967) Atlas of clinical laboratory procedures, vol. 1, Clinical chemistry. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 62–63
McKay E, Slater RJ (1962) Studies on human proteinuria. II, Some characteristics of the gamma globulins excreted in normal, exercise, postural and nephrotic proteinuria. J Clin Invest 41:1638–1652
O'Brien D, Ibbott FA (1964) Laboratory manuel of pediatric micro- and ultramicrobiochemical techniques. Harper and Row, New York, pp 260
Poortmans JR (1984) Exercise and renal function. Sports med 1:125–153
Poortmans JR, Haralambie G (1979) Biochemical changes in a 100 km run. Proteins in serum and urine. Eur J Appl Physiol 40:245–254
Poortmans JR, Jeanloz RW (1968) Quantitative immunochemical determination of twelve plasma proteins excreted in human urine collected before and after exercise. J Clin Invest 47:386–393
Siegel S (1956) Non parametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw Hill, Tokyo, pp 75–83
Todorovic B, Nikolic B, Brdoric R, Nikolic V, Stajakinovic B, Pavlovic-Kentera V. Proteinuria following submaximal work of constant and variable intensity. Int Z Angew Physiol 30:151–160
Von Krull F, Foellmer HG, Liebau H, Ehrich JHH (1984) Renale Adaptationsmechanismen bei körperlicher Belastung. D Z Sportmed 24–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poortmans, J.R., Labilloy, D. The influence of work intensity on postexercise proteinuria. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 57, 260–263 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00640673
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00640673