Summary
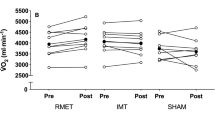
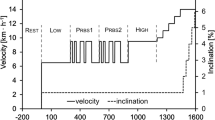
Recently, we have shown that an untrained respiratory system does limit the endurance of submaximal exercise (64% peak oxygen consumption) in normal sedentary subjects. These subjects were able to increase breathing endurance by almost 300% and cycle endurance by 50% after isolated respiratory training. The aim of the present study was to find out if normal, endurance trained subjects would also benefit from respiratory training. Breathing and cycle endurance as well as maximal oxygen consumption (\(\dot VO_{2 max} \)) and anaerobic threshold were measured in eight subjects. Subsequently, the subjects trained their respiratory muscles for 4 weeks by breathing 85-1601 · min−1 for 30 min daily. Otherwise they continued their habitual endurance training. After respiratory training, the performance tests made at the beginning of the study were repeated. Respiratory training increased breathing endurance from 6.1 (SD 1.8) min to about 40 min. Cycle endurance at the anaerobic threshold [77 (SD 6) %\(\dot VO_{2 max} \)] was improved from 22.8 (SD 8.3) min to 31.5 (SD 12.6) min while\(\dot VO_{2 max} \) and the anaerobic threshold remained essentially the same. Therefore, the endurance of respiratory muscles can be improved remarkably even in trained subjects. Respiratory muscle fatigue induced hyperventilation which limited cycle performance at the anaerobic threshold. After respiratory training, minute ventilation for a given exercise intensity was reduced and cycle performance at the anaerobic threshold was prolonged. These results would indicate the respiratory system to be an exercise limiting factor in normal, endurance trained subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen WK, Seals DR, Hurley BF, Ehsani AE, Hagberg JM (1985) Lactate threshold and distance-running performance in young and older endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 58:1281–1284
Anholm JD, Stray-Gundersen J, Ramanathan M, Johnson RL Jr (1989) Sustained maximal ventilation after endurance exercise in athletes. J Appl Physiol 67:1759–1763
Belman MJ, Gaesser GA (1988) Ventilatory muscle training in the elderly. J Appl Physiol 64:899–905
Boutellier U, Farhi LE (1986) Influence of breathing frequency and tidal volume on cardiac output. Respir Physiol 66:123–133
Boutellier U, Piwko P (1992) The respiratory system as an exercise limiting factor in normal sedentary subjects. Eur J Appl Physiol 64:145–152
Buess C, Pietsch P, Guggenbühl W, Koller EA (1986) A pulsed diagonal-beam ultrasonic airflow meter. J Appl Physiol 61:1195–1199
Casaburi R, Storer TW, Wasserman K (1987) Mediation of reduced ventilatory response to exercise after endurance training. J Appl Physiol 63:1533–1538
Conconi F, Ferrari M, Ziglio PG, Droghetti P, Codeca L (1982) Determination of the anaerobic threshold by a noninvasive field test in runners. J Appl Physiol 52:869–873
Dodd SL, Powers SK, Thompson D, Landry G, Lawler J (1989) Exercise performance following intense, short-term ventilatory work. Int J Sports Med 10:48–52
Fairbarn MS, Coutts KC, Pardy RL, McKenzie DC (1991) Improved respiratory muscle endurance of highly trained cyclists and the effects on maximal exercise performance. Int J Sports Med 12:66–70
Gimenez M, Cereceda V, Teculescu D, Aug F, Laxenaire MC (1982) Square-wave endurance exercise test (SWEET) for training and assessment in trained and untrained subjects, III. Effect on VO2max and maximal ventilation. Eur J Appl Physiol 49:379–387
Gleser MA, Vogel JA (1973) Endurance capacity for prolonged exercise on the bicycle ergometer. J Appl Physiol 34:438–442
Joyner M (1991) Modeling: optimal marathon performance on the basis of physiological factors. J Appl Physiol 70:683–687
Keens TG, Krastins IRB, Wannamaker EM, Levison H, Crozier DN, Bryan AC (1977) Ventilatory muscle endurance training in normal subjects and patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 116:853–860
Leith DE, Bradley M (1976) Ventilatory muscle strength and endurance training. J Appl Physiol 41:508–516
Mador MJ, Acevedo FA (1991a) Effect of respiratory muscle fatigue on breathing pattern during incremental exercise. Am Rev Respir Dis 143:462–468
Mador MJ, Acevedo FA (1991b) Effect of respiratory muscle fatigue on subsequent exercise performance. J Appl Physiol 70:2059–2065
Martin B, Heintzelman M, Chen H-I (1982) Exercise performance after ventilatory work. J Appl Physiol 52:1581–1585
Morgan DW, Kohrt WM, Bates BJ, Skinner JS (1987) Effects of respiratory muscle endurance training on ventilatory and endurance performance of moderately trained cyclists. Int J Sports Med 8:88–93
Norton KI, Delp MD, Prusaczyk WK, Armstrong RB (1989) A comparison of methods used to determine VO2 of exercising humans and animals. Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:480–486
Sachs L (1984) Angewandte Statistik, 6th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Stegemann J (1984) Leistungsphysiologie, 3rd edn. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York
Wasserman K, McIlroy MB (1964) Detecting the threshold of anaerobic metabolism. Am J Cardiol 14:844–852
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boutellier, U., Büchel, R., Kundert, A. et al. The respiratory system as an exercise limiting factor in normal trained subjects. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 65, 347–353 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868139
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868139