Abstract
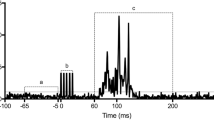
This study in humans tested the hypothesis that nociceptive muscle afferent input facilitates the occurrence of muscle cramps. In 13 healthy adults, muscle cramps were experimentally induced in the foot by stimulating the tibialis posterior nerve at the ankle with 2-s bursts of stimuli separated by 30 s, with stimulation frequency increasing by 2-Hz increments from 10 Hz until the cramp appeared. The minimum stimulation frequency that induced the cramp was defined “cramp frequency threshold”. In 2 days, elicitation of the cramp was performed in the two-feet with and without (baseline condition) injection of hypertonic (painful condition) or isotonic (control condition) saline into the deep midportion of the flexor hallucis brevis muscle, from where surface EMG signals were recorded. The cramp frequency threshold was lower for the painful condition with respect to its baseline (mean ± SE, hypertonic saline: 25.7 ± 2.1 Hz, corresponding baseline: 31.2 ± 2.8 Hz; P < 0.01) while there was no difference between the threshold with isotonic injection with respect to baseline. EMG average rectified value and power spectral frequency were higher during the cramp than immediately before the stimulation that elicited the cramp (pre-cramp: 13.9 ± 1.6 μV and 75.4 ± 3.8 Hz, respectively; post-cramp: 19.9 ± 3.2 μV and 101.6 ± 6.0 Hz; P < 0.05). The results suggest that nociceptive muscle afferent activity induced by injection of hypertonic saline facilitates the generation of electrically elicited muscle cramps.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreani CM, Hill JM, Kaufman MP (1997) Responses of group III and IV muscle afferents to dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol 82:1811–1817
Baldissera F, Cavallari P, Dworzak F (1994) Motor neuron ‘bistability’. A pathogenetic mechanism for cramps and myokymia. Brain 117:929–939
Bertolasi L, De Grandis D, Bongiovanni LG, Zanette GP, Gasperini M (1993) The influence of muscular lengthening on cramps. Ann Neurol 33:176–180
Campanini I, Merlo A, Degola P, Merletti R, Vezzosi G, Farina D (2007) Effect of electrode location on EMG signal envelope in leg muscles during gait. J Electromyogr Kinesiol (in press)
Denny-Brown D, Foley JM (1948) Myokymia and the benign fasciculation of muscular cramps. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 61:88–96
Gandevia SC (2001) Spinal and supraspinal factors in human muscle fatigue. Physiol Rev 81:1725–1789
Farina D, Gazzoni M, Merletti R (2003) Assessment of low back muscle fatigue by surface EMG signal analysis: methodological aspects. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 13:319–332
Farina D, Arendt-Nielsen L, Merletti R, Graven-Nielsen T (2004) Effect of experimental muscle pain on motor unit firing rate and conduction velocity. J Neurophysiol 91:1250–1259
Graven-Nielsen T, Mcardle A, Phoenix J, Arendt-Nielsen L, Jensen TS, Jackson MJ, Edwards RH (1997) In vivo model of muscle pain: quantification of intramuscular chemical, electrical, and pressure changes associated with saline-induced muscle pain in humans. Pain 69:137–143
Graven-Nielsen T, Lund H, Arent-Nielsen L, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bliddal H (2002) Inhibition of maximal voluntary contraction force by experimental muscle pain: a centrally mediated mechanism. Muscle Nerve 26:708–712
Hayward L, Wesselmann U, Rymer WZ (1991) Effects of muscle fatigue on mechanically sensitive afferents of slow conduction velocity in the cat triceps surae. J Neurophysiol 65:360–370
Jovanovic K, Anastasijevic R, Vuco J (1990) Reflex effects on gamma fusimotor neurones of chemically induced discharges in small diameter muscle afferents in decerebrate cats. Brain Res 521:89–94
Kastenbauer T, Irsigler P, Sauseng S, Grimm A, Prager R (2004) The prevalence of symptoms of sensorimotor and autonomic neuropathy in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic subjects. J Diabetes Complicat 18:27–31
Kaufman MP, Longhurst JC, Rybicki KJ, Wallach JH, Mitchell JH (1983) Effects of static muscular contraction on impulse activity of groups III and IV afferents in cats. J Appl Physiol 55:105–112
Kaufman MP, Rybicki KJ, Waldrop TG, Ordway GA (1984) Effect of ischemia on responses of group III and IV afferents to contraction. J Appl Physiol 57:644–650
Kendall FFP, Kendall E, McCreary BT (1993) Muscle testing and function Baltimore. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Kniffki KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF (1978) Responses of group IV afferent units from skeletal muscle to stretch, contraction and chemical stimulation. Exp Brain Res 61:511–522
Kumazawa T, Mizumura K (1977) Thin-fibre receptors responding to mechanical, chemical, and thermal stimulation in the skeletal muscle of the dog. J Physiol 273:179–194
Lambert E (1968) Electromyography in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In: Norris FH, Kurland LT (eds) Motor neuron diseases; research on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and related disorders. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 135–153
Laursen RJ, Graven-Nielsen T, Jensen TS, Arendt-Nielsen L (1999) The effect of differential and complete nerve block on experimental muscle pain in humans. Muscle Nerve 22:1564–1570
Layzer RB (1985) Diagnosis of neuromuscular disorders. In: Layzer RB (ed) Neuromuscular manifestation of systemic disease. Davis, Philadelphia, pp 19–22
Layzer RB, Rowland LP (1971) Cramps. N Engl J Med 285:31–40
Ljubisavljevic M, Anastasijevic R (1994) Fusimotor-induced changes in muscle spindle outflow and responsiveness in muscle fatigue in decerebrate cats. Neuroscience 63:339–348
Ljubisavljevic M, Arnastasljevic R, Trifunjagic D (1995) Changes in fusimotor discharge rate provoked by isotonic fatiguing muscle contractions in decerebrate cats. Brain Res 673:126–132
Masuda T, Miyano H, Sadoyama T (1985) The position of innervation zones in the biceps brachii investigated by surface electromyography. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 32:36–42
McGee SR (1990) Muscle cramps. Arch Intern Med 150:511–518
Mense S (1993) Nociception from skeletal muscle in relation to clinical muscle pain. Pain 54:241–289
Mense S, Stahnke M (1983) Responses in muscle afferent fibers of slow conduction velocity to contractions and ischemia in the cat. J Physiol 342:383–397
Mense S, Meyer H (1985) Different types of slowly conducting afferent units in cat skeletal muscle and tendon. J Physiol 363:403–417
Merletti R, Farina D, Granata A (1999) Non-invasive assessment of motor unit properties with linear electrode arrays. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 50:293–300
Miller TM, Layzer RB (2005) Muscle cramps. Muscle Nerve 32:431–442
Mills KR, Newham DJ, Edwards RHT (1982) Severe muscle cramps relieved by transcutaneous nerve stimulation: case report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:539–542
Norris FH, Gasteiger EL, Chatfield PO (1957) An electromyographic study of induced and spontaneous muscle cramps. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 9:139–147
Obi T, Mizoguchi K, Matsuoka H, Takatsu M, Nishimura Y (1993) Muscle cramp as the result of impaired GABA function—an electrophysiological and pharmacological observation. Muscle Nerve 16:1228–1231
Paintal AS (1960) Functional analysis of group III afferent fibres of mammalian muscles. J Physiol 152:250–270
Parisi L, Serrao M, Rossi P, Valente G, Fattaposta F, Pierelli F, Amabile G (2000) Afterdischarge activity in neuropathic patients with frequent muscle cramps. Acta Neurol Scand 102:359–362
Parisi L, Amabile G, Valente G, Calandriello E, Fattapposta F, Rossi P, Pierelli F, Serrao M (2003) Muscular cramps: a new proposal of classification. Acta Neurol Scand 107:176–186
Roeleveld K, Van Engelen BGM, Stegeman DF (2000) Possible mechanisms of muscle cramp form temporal and spatial surface EMG characteristics. J Appl Physiol 88:1698–1706
Ross BH, Thomas CK (1995) Human motor unit activity during induced muscle cramp. Brain 118(Pt 4):983–993
Rossi A, Decchi B (1997) Changes in Ib heteronymous inhibition to soleus motoneurones during cutaneous and muscle nociceptive stimulation in humans. Brain Res 774:55–61
Rossi A, Decchi B, Ginanneschi F (1999) Presynaptic excitability changes of group Ia fibres to muscle nociceptive stimulation in humans. Brain Res 818:12–22
Rowland LP (1985) Cramps, spasms and muscle stiffness. Rev Neurol 141:261–273
Saito M, Suehara M, Nagata A, Kanzato N, Arimura K (1998) Afterdischarges following F waves observed in a patient with tetanus. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 38:377–380
Schwellnus MP (1999) Skeletal muscle cramps during exercise. Phys Sportsmed 27:109–115
Sejersted OM, Sjogaard G (2000) Dynamics and consequences of potassium shifts in skeletal muscle and heart during exercise. Physiol Rev 80:1411–1481
Serrao M, Rossi P, Cardinali P, Valente G, Parisi L, Pierelli F (2000) Gabapentin treatment for muscle cramps: an open-label trial. Clin Neuropharmacol 40:45–49
Serratrice G, Mei N, Pellissier JF, Cros D (1980) Cutaneous and muscular unmyelinated afferent fibres. Clinical, histological and experimental study. Possible explanation of muscular cramps. Sem Hop 56:665–670
Stone MB, Edwards JE, Babington JP, Ingersoll CD, Palmieri RM (2003) Reliability of an electrical method to induce muscle cramp. Muscle Nerve 27:122–123
Svensson P, Graven-Nielsen T, Matre DA, Arendt-Nielsen L (1998) Experimental muscle pain does not cause long-lasting increases in resting EMG activity. Muscle Nerve 21:1382–1389
Wolfe GI, Barohon RJ (2002) Painful peripheral neuropathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol 4:177–188
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serrao, M., Arendt-Nielsen, L., Ge, HY. et al. Experimental muscle pain decreases the frequency threshold of electrically elicited muscle cramps. Exp Brain Res 182, 301–308 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-0985-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-0985-1