Abstract
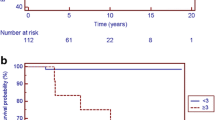
Our aim was to identify prognostic factors for an arrhythmic event (AE) in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) without a previous AE. One hundred thirty-one nonconsecutive patients (≤20 years) with HCM but no previous AE were evaluated at the NIH Clinical Center from 1980 to 2001. At a median follow-up of 6.4 years, 22 patients experienced an AE [sudden death (SD) (n = 12), resuscitated cardiac arrest (n = 3), clinical sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) (n = 2), and implantable cardiac defibrillator discharge (n = 5)], resulting in a 2% annual AE rate. Baseline factors that were most predictive in univariate risk analysis included ventricular septal thickness (ST) (P = 0.01), VT induction by programmed ventricular stimulation (PVS) (P = 0.01), age (P = 0.05), and presyncope/syncope (P = 0.05). In multivariate analysis, ST, age, presyncope/syncope, and PVS were not independently predictive of risk for an AE. However, the 5-year event rates for AE was 15% (95% CI: 5–23%) if ST ≥ 20 mm, 19% (95% CI: 6–31%) when age ≥ 13 years and ST ≥ 20 mm were combined together, and 23% (95% CI: 3–39%) when PVS and ST ≥ 20 mm were combined together. Of the various risk factors that were considered in our pediatric HCM cohort, ST and inducible VT were the most significant univariate predictors of risk for an AE. More traditional risk factors identified in older patients (family history of SD, VT on Holter, and exercise-induced hypotension) were not predictive of an AE in patients age under 21 years.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander ME, Walsh EP, Saul JP, Epsein MR, Triedman JK (1999) Value of programmed ventricular stimulation in patients with congenital heart disease. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 10:1033–1044
Alexander ME, Cecchin F, Walsh EP, Triedman JK, Bevilacqua, Berul CI (2004) Implications of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in congenital heart disease and pediatrics. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15:72–76
Anderson KP, Stinson EB, Derby GC, Oyer PE, Mason JW (1983) Vulnerability of patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy to ventricular arrhythmia induction in the operating room. Analysis of 17 patients. Am J Cardiol 51:811–816
Basso C, Thiene G, Corrado D, Buja G, Melacini P, Nava A (2000) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and sudden death in the young: pathologic evidence of myocardial ischemia. Hum Pathol 31:988–998
Begley DA, Mohiddin SA, Tripodi D, Winkler JB, Fananapazir L (2003) Efficacy of implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy for primary and secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 26:1887–1896
Brito D, Richard P, Isnard R, Pipa J, Komajda M, Madeira H (2003) Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: the same mutation, different prognosis. Comparison of two families with long follow-up. Rev Port Cardiol 22:1445–1461
Buxton AE, Lee KL, Fisher JD, Josephson ME, Prystowsky EN, Hafley G (1999) A randomized study of the prevention of sudden death in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 341:1882–1890
Buxton AE, Lee KL, DiCarlo L, Gold MR, Greer GS, Prystowsky EN, O’Toole MF, Tang A, Fisher JD, Coromilas J, Talajic M, Hafley G (2000) Electrophysiologic testing to identify patients with coronary artery disease who are at risk for sudden death. N Engl J Med 342:1937–1945
Cecchi F, Olivotto I, Montereggi A, Squillatini G, Dolara A, Maron BJ (1998) Prognostic value of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia and the potential role of amiodarone treatment in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: assessment in an unselected non-referral based patient population. Heart 79:331–336
Cha YM, Gersh BJ, Maron BJ, Boriani G, Spirito P, Hodge DO, Weivoda PL, Trusty JM, Friedman PA, Hammill SC, Rea RF, Shen WK (2007) Electrophysiologic manifestations of ventricular tachyarrhythmias provoking appropriate defibrillator interventions in high-risk patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 18:483–487
Colan SD, Lipshultz SE, Lowe AM, Sleeper LA, Messere J, Cox GF, Lurie PR, Orav EJ, Towbin JA (2007) Epidemiology and cause-specific outcome of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children. Findings from the pediatric cardiomyopathy registry. Circulation 15:773–781
Decker JA, Rossano JW, Smith EO, Cannon B, Clunie SK, Gates C, Jefferies J, Kim J, Price JF, Dreyer WJ, Towbin JA, Denfield SW (2009) Risk factors and mode of death in isolated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in children. J Am Coll Cardiol 54:250–254
Dilsizian V, Bonow R, Epstein SE, Fananapazir L (1993) Myocardial ischemia detected by thallium scintigraphy is frequently related to cardiac arrest and syncope in young patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:796–804
Elliott PM, Poloniecki J, Dickie S, Sharma S, Monserrat L, Varnava A, Mahon NG, McKenna WJ (2000) Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: identification of high risk patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2212–2218
Elliott PM, Gimeno Blanes JR, Mahon NJ, Poloniecki JD, McKenna WJ (2001) Relation between severity of left ventricular hypertrophy and prognosis in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 357:420–424
Fananapazir L, Tracy CM, Leon MB, Winkler JB, Cannon RO 3rd, Bonow RO, Maron BJ, Epstein SE (1989) Electropysiologic abnormalities in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A consecutive analysis in 155 patients. Circulation 80:1259–1268
Frenneaux MP (2004) Assessing the risk of sudden cardiac death in a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 90:570–575
Geibel A, Brugada P, Zehender M, Stevenson W, Waldecker B, Wellens HJJ (1987) Value of programmed electrical stimulation using a standardized ventricular stimulation protocol in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 60:738–739
Greenberg SL, Mauricio Sánchez J, Cooper JA, Cain ME, Chen J, Gleva MJ, Lindsay BD, Smith TW, Faddis MN (2007) Sustained polymorphic arrhythmias induced by programmed ventricular stimulation have prognostic value in patients receiving defibrillators. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 30:1067–1075
Hinkle LE, Thaler HT, Merke DP, Renier-Berg D, Morton NE (1988) The risk factors for arrhythmic death in a sample of men followed for 20 years. Am J Epidemiol 127:500–515
Jansson K, Dahlstrom U, Karlsson E, Nylander E, Walfridsson H, Sonnhag C (1990) The value of exercise test, Holter monitoring, and programmed electrical stimulation in detection of ventricular arrhythmias in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 13:1261–1267
Khairy P, Landzberg MJ, Gatzoulis MA, Lucron H, Lambert J, Marçon F, Alexander ME, Walsh EP (2004) Value of programmed ventricular stimulation after tetralogy of Fallot repair: a multicenter study. Circulation 109:1994–2000
Kleemann T, Becker T, Doenges K, Vater M, Senges J, Schneider S, Saggau W, Weisse U, Seidl K (2007) Annual rate of transvenous defibrillation lead defects in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators over a period of >10 years. Circulation 115:2474–2480
Kowey PR, Eisenberg R, Engel TR (1984) Sustained arrhythmias in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 310:1566–1569
Krikler DM, Davies MJ, Fowland E, Goodwin JF, Evans RC, Shaw DB (1980) Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: associated accessory atrioventricular pathways. Br Heart J 43:245–251
Kuck KH, Kunze KP, Schluter M, Nienaber CA, Costard A (1988) Programmed electrical stimulation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Results in patients with and without cardiac arrest or syncope. Eur Heart J 9:177–185
Lim PO, Morris-Thurgood JA, Frenneaux MP (2002) Vascular mechanisms of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, including blood pressure responses to exercise. Cardiol Rev 10:15–23
Lin G, Nishimura RA, Gersh GJ, Phil D, Ommen SR, Ackerman MJ, Brady PA (2009) Device complications and inappropriate implantable cardioverter defibrillator shocks in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 95:709–714
Maron BJ, Shen WK, Link MS, Epstein AE, Almquist AK, Daubert JP, Bardy GH, Favale S, Rea RF, Boriani G, Estes NA 3rd, Spirito P (2000) Efficacy of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators for the prevention of sudden death in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 342:365–373
Maron BJ, Spirito P, Shen WK, Haas TS, Formisano F, Link MS, Epstein AE, Almquist AK, Daubert JP, Lawrenz T, Boriani G, Estes NA III, Favale S, Piccininno M, Winters SL, Santini M, Betocchi S, Arribas F, Sherrid MV, Buja G, Semsarian C, Bruzzi P (2007) Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and prevention of sudden cardiac death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. JAMA 298:405–412
Maron BJ, Haas TS, Shannon KM, Almquist AK, Hodges JS (2009) Long term survival after cardiac arrest in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm 6:993–997
McKenna WJ, Deanfield JE (1984) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an important cause of sudden death. Arch Dis Child 59:971–975
McKenna WJ, Franklin RC, Nihoyannopoulos P, Robinson KC, Deanfield JE (1988) Arrhythmia and prognosis in infants, children and adolescents with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiolol 11:147–153
McLeod CJ, Ackerman MJ, Nishimura RA, Tajik AJ, Gersh BJ, Ommen SR (2009) Outcome of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and a normal electrocardiogram. J Am Coll Cardiolol 54:229–233
Melacini P, Maron BJ, Bobbo F, Basso C, Tokajuk B, Thiene G, Iliceto S (2007) Evidence that pharmacologic strategies lack efficacy for the prevention of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 93:708–710
Mohiddin SA, Begley D, Shih J, Fananapazir L (2000) Myocardial bridging does not predict sudden death in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy but is associated with more severe cardiac disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:2270–2278
Monserrat L, Elliott PM, Gimeno JR, Sharma S, Penas-Lado M, McKenna WJ (2003) Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: an independent marker of sudden death risk in young patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:873–879
Olivotto I, Maron BJ, Montereggi A, Mazzuoli F, Dolara A, Cecchi F (1999) Prognostic value of systemic blood pressure response during exercise in a community-based patient population with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 33:2044–2051
Olivotto I, Gistri R, Petrone P, Pedemonte E, Vargiu D, Cecchi F (2003) Maximum left ventricular thickness and risk of sudden death in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 41:315–321
Östman-Smith I, Wettrell G, Keeton B, Riesenfeld T, Holmgren D, Ergander U (2005) Echocardiographic and electrocardiographic identification of those children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy who should be considered at high-risk of dying suddenly. Cardiol Young 15:632–642
Östman-Smith I, Wettrell G, Keeton B, Holmgren D, Ergander U, Gould S, Bowker C, Verdicchio M (2008) Age and gender-specific mortality rates in childhood hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 29:1160–1167
Pablo Kaski JP, Tome Esteban MT, Lowe M, Sporton S, Rees P, Deanfield JE, McKenna WJ, Elliott PM (2007) Outcomes after implantable cardioverter-defibrillator treatment in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 93:372–374
Roguin A, Bomma CS, Nasir K, Tandri H, Tichnell C, James C, Rutberg J, Crosson J, Spevak PJ, Berger RD, Halperin HR, Calkins H (2004) Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:1843–1852
Romero-Farina G, Candell-Riera J, Pereztol-Valdés O, Castell J, Aguadé S, Galve E, Palet J, Oller-Martínez G, Armadans L, Reina D, Soler-Soler J (2001) Myocardial perfusion SPECT and isotopic ventriculography in obstructive and non-obstructive hypertrophic myocardiopathy. Rev Esp Med Nucl 20:530–536
Sadoul N, Prasad K, Elliott PM, Bannerjee S, Frenneaux MP, McKenna WJ (1997) Prospective prognostic assessment of blood pressure response during exercise in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 96:2987–2991
Saumarez RC, Slade AK, Grace AA, Sadoul N, Camm AJ, McKenna WJ (1995) The significance of paced electrogram fractionation in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a prospective study. Circulation 91:2762–2768
Schiavone WA, Maliney JD, Lever HM, Castle LW, Sterba R, Morant V (1986) Electrophysiologic studies of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy presenting with syncope of undetermined etiology. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 9:476–481
Sorajja P, Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Gersh BJ, Tajik AJ, Holmes DR (2003) Myocardial bridging in adult patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 42:889–894
Spirito P, Bellone P, Harris KM, Bernabo P, Bruzzi P, Maron BJ (2000) Magnitude of left ventricular hypertrophy and risk of sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 342:1778–1785
Thomas HL, Morris-Thurgood J, Atherton J, McKenna WJ, Frenneaux MP (1998) Reflex responses of venous capacitance vessels in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Clin Sci 94:339–346
Wellens JHH, Bar FW, Vanagt EJ (1980) Death after ajmaline administration. Am J Cardiol 45:905
Woo A, Monakier D, Harris L, Hill A, Shah P, Douglas Wigle E, Rakowski H, Rozenblyum E, Cameron DA (2007) Determinants of implantable defibrillator discharges in high risk patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 93:1044–1045
Yetman AT, McCrindle BW, MacDonald C, Freedom RM, Gow R (1998) Myocardial bridging in children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a risk factor for sudden death. N Engl J Med 339:1201–1209
Zhu DWX, Sun H, Hill R, Roberts R (1998) The value of electrophysiologic study and prophylactic implantation of cardioverter defibrillator in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 21:299–302
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by intramural research funds from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, NIH, Bethesda, MD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moak, J.P., Leifer, E.S., Tripodi, D. et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Risk Factors for Adverse Arrhythmic Events. Pediatr Cardiol 32, 1096–1105 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9967-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-9967-y