Abstract
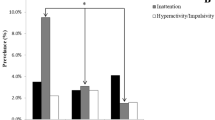
This study aimed to determine the causes of sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) in apparently healthy children at a single center in the era of primary prevention (screening questionnaire [SQ]) and secondary prevention (automated external defibrillator [AED] and the automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator [AICD]). Any child 0 to 18 years of age without prior known disease, except for attention deficit disorder, who underwent out-of-the hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation was included in the study as a SCA subject. A retrospective chart review was used to evaluate the efficacy of the SQ, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest roentgenogram (CXR), and echocardiogram. The findings showed that for 44 of 6,656 children admitted to intensive care with SCA, an AED was used for 39 %, an AICD was placed in 18 %,and survival to hospital discharge was 50 %. The etiology for SCA was identified in 57 % of the cases, mostly in those older than 1 year, and the majority of these had a cardiac etiology (50 %), whereas 7 % had rupture of an arteriovenous malformation. Stimulant medication use was seen in 11 % of the SCA subjects. In the best-case scenario of hypothesized primary prevention, a prior SQ, CXR, ECG, or echocardiogram may have detected respectively 18, 9, 23 and 16 % of the at-risk cases, and 32 % of the cases may have been detected with ECG and SQ together. Based on a historical control cohort, a positive ECG was significantly higher in the children with SCA (p = 0.014). An ECG together with a screening SQ may be more effective in identifying children potentially at risk for SCA than an SQ alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Lafuente R, Aguilera B, Suarez-Mier MA, Morentin B, Vallejo G, Gomez J, Fernandez-Rodriguez A (2008) Detection of human herpesvirus-6, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus in formalin-fixed tissues from sudden infant death: a study with quantitative real-time PCR. Forensic Sci Int 178(2–3):106–111
American Academy of Pediatrics (2000) Clinical practice guideline: diagnosis and evaluation of the child with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 105(5):1158–1170
American Academy of Pediatrics (2012) Pediatric sudden cardiac arrest. Pediatrics 129(4):e1094–e1102
Bader RS, Goldberg L, Sahn DJ (2004) Risk of sudden cardiac death in young athletes: which screening strategies are appropriate? Pediatr Clin North Am 51(5):1421–1441
Behr ER, Casey A, Sheppard M, Wright M, Bowker TJ, Davies MJ, McKenna WJ, Wood DA (2007) Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome: a national survey of sudden unexplained cardiac death. Heart 93(5):601–605
Behr ER, Dalageorgou C, Christiansen M, Syrris P, Hughes S, Tome Esteban MT, Rowland E, Jeffery S, McKenna WJ (2008) Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome: familial evaluation identifies inheritable heart disease in the majority of families. Eur Heart J 29(13):1670–1680
Bents RT, Tokish JM, Goldberg L (2004) Ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, and amphetamine prevalence in college hockey players: most report performance-enhancing use. Phys Sportsmed 32(9):30–34
Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Wilens TE, Prince JB, Faraone SV (2006) Treatment of ADHD with stimulant medications: response to Nissen perspective in the New England Journal of Medicine. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 45(10):1147–1150
Byard RW, James RA, Gilbert JD (2002) Childhood sporting deaths. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 23(4):364–367
Campbell RM, Berger S (2006) Preventing pediatric sudden cardiac death: where do we start? Pediatrics 118(2):802–804
Cave DM, Aufderheide TP, Beeson J, Ellison A, Gregory A, Hazinski MF, Hiratzka LF, Lurie KG, Morrison LJ, Mosesso VN Jr, et al (2011) Importance and implementation of training in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and automated external defibrillation in schools: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 123(6):691–706
Cooper WO, Habel LA, Sox CM, Chan KA, Arbogast PG, Cheetham TC, Murray KT, Quinn VP, Stein CM, Callahan ST et al (2011) ADHD drugs and serious cardiovascular events in children and young adults. N Engl J Med 365(20):1896–1904
Drezner JA, Fudge J, Harmon KG, Berger S, Campbell RM, Vetter VL (2012) Warning symptoms and family history in children and young adults with sudden cardiac arrest. J Am Board Fam Med 25(4):408–415
Dulcan M (1997) Practice parameters for the assessment and treatment of children, adolescents, and adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(10 Suppl):85S–121S
Gillette PC, Garson A Jr (1992) Sudden cardiac death in the pediatric population. Circulation 85(1 Suppl):I64–I69
Gould JB, Lee AF, Morelock S (1988) The relationship between sleep and sudden infant death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 533:62–77
Gould MS, Walsh BT, Munfakh JL, Kleinman M, Duan N, Olfson M, Greenhill L, Cooper T (2009) Sudden death and use of stimulant medications in youths. Am J Psychiatry 166(9):992–1001
Hammerness P, Wilens T, Mick E, Spencer T, Doyle R, McCreary M, Becker J, Biederman J (2009) Cardiovascular effects of longer-term, high-dose OROS methylphenidate in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Pediatr 155(1):84–89, 89 e81
Knight M (2007) Stimulant-drug therapy for attention-deficit disorder (with or without hyperactivity) and sudden cardiac death. Pediatrics 119(1):154–155
Leslie LK, Alexander ME, Trikalinos TA, Cohen JT, Parsons SK, Newburger JW (2008) Reexamining the emperor’s new clothes: ambiguities in current cardiac screening recommendations for youth with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 1(2):134–137
Liberthson RR (1996) Sudden death from cardiac causes in children and young adults. N Engl J Med 334(16):1039–1044
Matschke J, Lockemann U, Schulz F (2007) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations presenting as sudden unexpected death: a report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 28(2):173–176
Rimsza ME, Newberry S (2008) Unexpected infant deaths associated with use of cough and cold medications. Pediatrics 122(2):e318–e322
Rodday AM, Triedman JK, Alexander ME, Cohen JT, Ip S, Newburger JW, Parsons SK, Trikalinos TA, Wong JB, Leslie LK (2012) Electrocardiogram screening for disorders that cause sudden cardiac death in asymptomatic children: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics 129(4):e999–e1010
Rowland AS, Lesesne CA, Abramowitz AJ (2002) The epidemiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a public health view. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 8(3):162–170
Samuels JA, Franco K, Wan F, Sorof JM (2006) Effect of stimulants on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in children with ADHD: a double-blind, randomized, cross-over trial. Pediatr Nephrol 21(1):92–95
Schelleman H, Bilker WB, Strom BL, Kimmel SE, Newcomb C, Guevara JP, Daniel GW, Cziraky MJ, Hennessy S (2011) Cardiovascular events and death in children exposed and unexposed to ADHD agents. Pediatrics 127(6):1102–1110
Silka MJ, Kron J, Dunnigan A, Dick M II (1993) Sudden cardiac death and the use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in pediatric patients. The Pediatric Electrophysiology Society. Circulation 87(3):800–807
Swenson JM, Fischer DR, Miller SA, Boyle GJ, Ettedgui JA, Beerman LB (1997) Are chest radiographs and electrocardiograms still valuable in evaluating new pediatric patients with heart murmurs or chest pain? Pediatrics 99(1):1–3
Taylor AJ, Rogan KM, Virmani R (1992) Sudden cardiac death associated with isolated congenital coronary artery anomalies. J Am Coll Cardiol 20(3):640–647
Tester DJ, Ackerman MJ (2006) The role of molecular autopsy in unexplained sudden cardiac death. Curr Opin Cardiol 21(3):166–172
Vennemann M, Bajanowski T, Butterfass-Bahloul T, Sauerland C, Jorch G, Brinkmann B, Mitchell EA (2007) Do risk factors differ between explained sudden unexpected death in infancy and sudden infant death syndrome? Arch Dis Child 92(2):133–136
Vetter VL, Elia J, Erickson C, Berger S, Blum N, Uzark K, Webb CL (2008) Cardiovascular monitoring of children and adolescents with heart disease receiving stimulant drugs: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee and the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Circulation 117(18):2407–2423
Wreford FS, Conradi SE, Cohle SD, Lie JT, Dana SE, Puri S (1991) Sudden death caused by coronary artery aneurysms: a late complication of Kawasaki disease. J Forensic Sci 36(1):51–59
Yusin AS (2004) 2001 American Academy of Pediatrics practice parameter on attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 113(2):428–429 discussion 428–429
Acknowledgments
The described project was partially supported by Grant No. K23HL089391 (Determination of genetics of childhood onset hypertension, PI Monesha Gupta) from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute or the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alapati, S., Strobel, N., Hashmi, S. et al. Sudden Unexplained Cardiac Arrest in Apparently Healthy Children: A Single-Center Experience. Pediatr Cardiol 34, 639–645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0516-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0516-0