Abstract.
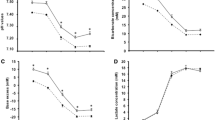
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of alkalosis on epinephrine concentrations in response to a 90 s maximal exercise test. A group of ten healthy men ingested either a bicarbonate (BS) supplement (0.3 g·kg–1 of body mass of sodium bicarbonate) or placebo mixture (P) prior to performing a 90 s maximal cycle ergometer test. An indwelling Teflon cannula was placed in the antecubital vein and blood samples were drawn at three times at rest separated by 10 min, immediately following the protocol, and at 2.5, 5, and 10 min post exercise to determine plasma epinephrine concentrations. Sodium bicarbonate ingestion significantly (P<0.05) induced alkalosis both at rest [mean (SD) pH=7.42 (0.02) BS, 7.38 (0.02) P] and after the exercise protocol [pH=7.16 (0.02) BS, 7.12 (0.02) P]. Plasma epinephrine concentrations were not significantly different immediately post exercise between the two conditions [4.2 (0.6) compared to 4.2 (0.7) pmol·ml–1 in BS and P, respectively]. Work performed and power output attained were not significantly different between the two treatment conditions [mean power=258.7 (35.1) W BS, 260.3 (35.4) W P; peak power=534.7 (61.6) W BS, 535.7 (54.4) W P]. The primary finding of this investigation was that orally-induced alkalosis does not significantly affect plasma epinephrine concentrations or performance following 90 s of maximal cycle exercise in untrained men.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marx, J.O., Gordon, S.E., Vos, N.H. et al. Effect of alkalosis on plasma epinephrine responses to high intensity cycle exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 87, 72–77 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0591-7
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0591-7