Abstract.
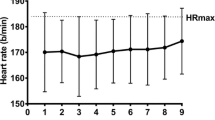
The purpose of this study was, firstly, to investigate the intensity of exercise performanceof highly trained ultra-endurance triathletes during the cycling portion of an Ironman triathlon, and, secondly, to examine the anaerobic threshold and its relationship to this performance. Following a peak oxygen consumption (VO2peak) test on a cycle ergometer to determine the heart rate (HRTh,vent) and power output (POTh,vent) at the ventilatory threshold (Thvent), 11 highly trained male triathletes [mean (SEM) age 35.8 (1.6) years, body fat 11.7 (1.2)%. VO2peak 67.5 (1.0) ml·kg–1·min–1] who were participating in an Ironman triathlon, in random order: (1) cycled at their POTh,vent (BiTh,vent) until they were exhausted, and (2) cycled for 5 h at a self-selected intensity (BiSSI). Cycling power output (PO), oxygen uptake (VO2), heart rate (HR) and blood lactate concentration ([La–]b) were recorded at regular intervals during these trials, while performance HR was recorded during the cycling phase of the Ironman triathlon. Significantly greater (P<0.05) values were attained during BiTh,vent than during BiSSI for PO [274 (9) compared to 188 (9) W], VO2 [3.61 (0.15) compared to 2.64 (0.09) l·min–1], and [La–]b [6.7 (0.8) compared to 2.8 (0.4) mmol·l–1]. Moreover, mean HR during the Ironman triathlon cycle phase [146.3 (2.4) beats·min–1; n=7] was significantly greater than mean HR during BiSSI [130 (4) beats·min–1], and significantly less than mean HR during BiTh,vent [159 (3) beats·min–1; all P<0.05]. However, HR during the cycle portion of the Ironman triathlon was highly related to (r=0.873; P<0.05) and not significantly different to HRTh,vent [150 (4) beats·min–1]. These data suggest that ultra-endurance triathletes cycle during the Ironman triathlon at a HR intensity that approximates to HRTh,vent, but at a PO that is significantly below POTh,vent.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laursen, P.B., Rhodes, E.C., Langill, R.H. et al. Relationship of exercise test variables to cycling performance in an Ironman triathlon. Eur J Appl Physiol 87, 433–440 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0659-4
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0659-4