Abstract
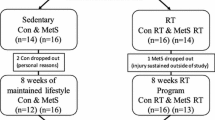
Resistance training is widely recommended to prevent sarcopenia and osteoporosis. However, the effects of upper and lower limb resistance training on arterial stiffness are unclear. The present study investigates the effects of upper and lower limbs resistance training on arterial stiffness. Thirty young healthy subjects (male 19, female 11, aged 20.1 ± 0.4 years, mean ± SD) were randomly assigned to upper limb RT group (upper limb group, n = 10, male 7, female 3), lower limb RT group (lower limb group, n = 10, male 7, female 3) and sedentary groups (n = 10, male 6, female 4). The upper and lower limb groups performed RT at 80% of one repetition maximum twice each week for 10 weeks. Arterial stiffness was measured by brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV). In addition, we measured plasma norepinephrine (NE) concentration. baPWV after training in the upper limb group had significantly increased from baseline (P < 0.05). In addition, plasma NE concentration after training in the upper limb group had significantly increased from baseline (P < 0.05). No such changes were observed in the lower limb and sedentary groups. Moreover, a significant positive correlation between baPWV and plasma NE concentration in upper limb group was observed (P < 0.05). In contrast, no significant correlation between baPWV and plasma NE concentration in lower limb and sedentary groups was observed. These findings suggested that upper limbs resistance training increases plasma NE concentration and promotes the increase of arterial stiffness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aso K, Miyata M, Kubo T, Hashiguchi H, Fukudome M, Fukushige E, Koriyama N, Nakazaki M, Minagoe S, Tei C (2003) Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity is useful for evaluation of complications in type 2 diabetic patients. Hypertens Res 26:807–813. doi:10.1291/hypres.26.807
Beaty O III (1985) Carotid sinus and blood pressure control during hindlimb and forelimb contractions. Am J Physiol 248:H688–H694
Blacher J, Guerin AP, Pannier B, Marchais SJ, Safar ME, London GM (1999) Impact of aortic stiffness on survival in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 99:2434–2439
Boulpaep EL (2003) Arteries and veins. In: Boron WF, Boulpaep EL (eds) Medical physiology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 447–462
Casey DP, Beck DT, Braith RW (2007) Progressive resistance training without volume increases does not alter arterial stiffness and aortic wave reflection. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 232:1228–1235. doi:10.3181/0703-RM-65
Collier SR, Kanaley JA, Carhart R Jr, Frechette V, Tobin MM, Hall AK, Luckenbaugh AN, Fernhall B (2008) Effect of 4 weeks of aerobic or resistance exercise training on arterial stiffness, blood flow and blood pressure in pre- and stage-1 hypertensives. J Hum Hypertens 22:678–686. doi:10.1038/jhh.2008.36
Cortez-Cooper MY, DeVan AE, Anton MM, Farrar RP, Beckwith KA, Todd JS, Tanaka H (2005) Effects of high intensity resistance training on arterial stiffness and wave reflection in women. Am J Hypertens 18:930–934. doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.01.008
Franklin BA, Bonzheim K, Gordon S, Timmis GC (1996) Snow shoveling: a trigger for acute myocardial infarction and sudden coronary death. Am J Cardiol 77:855–858. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(97)89181-3
Heffernan KS, Rossow L, Jae SY, Shokunbi HG, Gibson EM, Fernhall B (2006) Effect of single-leg resistance exercise on regional arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 98:185–190. doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0259-9
Heffernan KS, Jae SY, Lee M, Woods JA, Fernhall B (2008) Arterial wave reflection and vascular autonomic modulation in young and older men. Aging Clin Exp Res 20:1–7
Joyner MJ, Nauss LA, Warner MA, Warner DO (1992) Sympathetic modulation of blood flow and O2 uptake in rhythmically contracting human forearm muscles. Am J Physiol 263:H1078–H1083
Kawano H, Tanaka H, Miyachi M (2006) Resistance training and arterial compliance: keeping the benefits while minimizing the stiffening. J Hypertens 24:1753–1759. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000242399.60838.14
Kobayashi K, Akishita M, Yu W, Hashimoto M, Ohni M, Toba K (2004) Interrelationship between non-invasive measurements of atherosclerosis: flow-mediated dilation of brachial artery, carotid intima-media thickness and pulse wave velocity. Atherosclerosis 173:13–18. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2003.10.013
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker-Boudier H, European network for non-invasive investigation of large arteries (2006) Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 27:2588–2605. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl254
London GM, Guerin AP (1999) Influence of arterial pulse and reflected waves on blood pressure and cardiac function. Am Heart J 138:220–224. doi:10.1016/S0002-8703(99)70313-3
Maeda S, Otsuki T, Iemitsu M, Kamioka M, Sugawara J, Kuno S, Ajisaka R, Tanaka H (2006) Effects of leg resistance training on arterial function in older men. Br J Sports Med 40:867–869. doi:10.1136/bjsm.2006.029538
Mimura T, Takenaka T, Kanno Y, Moriwaki K, Okada H, Suzuki H (2008) Vascular compliance is secured under angiotensin inhibition in non-diabetic chronic kidney diseases. J Hum Hypertens 22:38–47. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1002264
Miyachi M, Kawano H, Sugawara J, Takahashi K, Hayashi K, Yamazaki K, Tabata I, Tanaka H (2004) Unfavorable effects of resistance training on central arterial compliance: a randomized intervention study. Circulation 110:2858–2863. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000146380.08401.99
Munakata M, Ito N, Nunokawa T, Yoshinaga K (2003) Utility of automated brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity measurements in hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens 16:653–657. doi:10.1016/S0895-7061(03)00918-X
Munakata M, Nunokawa T, Yoshinaga K, Toyota T, J-TOPP Study Group (2006) Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity is an independent risk factor for microalbuminuria in patients with essential hypertension—a Japanese trial on the prognostic implication of pulse wave velocity (J-TOPP). Hypertens Res 29:515–521. doi:10.1291/hypres.29.515
Nakao M, Nomura K, Karita K, Nishikitani M, Yano E (2004) Relationship between brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity and heart rate variability in young Japanese men. Hypertens Res 27:925–931. doi:10.1291/hypres.27.925
Nieman DC, Henson DA, Sampson CS, Herring JL, Suttles J, Conley M, Stone MH, Butterworth DE, Davis JM (1995) The acute immune response to exhaustive resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med 16:322–328. doi:10.1055/s-2007-973013
Okamoto T, Masuhara M, Ikuta K (2006) Effects of eccentric and concentric resistance training on arterial stiffness. J Hum Hypertens 20:348–354. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001979
Paini A, Boutouyrie P, Calvet D, Tropeano AI, Laloux B, Laurent S (2006) Carotid and aortic stiffness: determinants of discrepancies. Hypertension 47:371–376. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000202052.25238.68
Pannier BM, Avolio AP, Hoeks A, Mancia G, Takazawa K (2002) Methods and devices for measuring arterial compliance in humans. Am J Hypertens 15:743–753. doi:10.1016/S0895-7061(02)02962-X
Pivarnik JM, Grafner TR, Elkins ES (1988) Metabolic, thermoregulatory, and psychophysiological responses during arm and leg exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:1–5. doi:10.1249/00005768-198802000-00001
Pollock ML, Franklin BA, Balady GJ, Chaitman BL, Fleg JL, Fletcher B, Limacher M, Piña IL, Stein RA, Williams M, Bazzarre T (2000) Resistance exercise in individuals with and without cardiovascular disease: benefits, rationale, safety, and prescription. Circulation 101:828–833
Pratley R, Nicklas B, Rubin M, Miller J, Smith A, Smith M, Hurley B, Goldberg A (1994) Strength training increases resting metabolic rate and norepinephrine levels in healthy 50- to 65-yr-old men. J Appl Physiol 76:133–137. doi:10.1063/1.357118
Raastad T, Glomsheller T, Bjøro T, Hallén J (2001) Changes in human skeletal muscle contractility and hormone status during 2 weeks of heavy strength training. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:54–63. doi:10.1007/s004210000328
Rakobowchuk M, McGowan CL, de Groot PC, Bruinsma D, Hartman JW, Phillips SM, MacDonald MJ (2005) Effect of whole body resistance training on arterial compliance in young men. Exp Physiol 90:645–651. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2004.029504
Ray CA, Mark AL (1993) Augmentation of muscle sympathetic nerve activity during fatiguing isometric leg exercise. J Appl Physiol 75:228–232
Ray CA, Rea RF, Clary MP, Mark AL (1992) Muscle sympathetic nerve responses to static leg exercise. J Appl Physiol 73:1523–1529
Rowell LB (1993) Human cardiovascular control. Oxford University Press, New York
Rowell LB, O’Leary DS (1990) Reflex control of the circulation during exercise: chemoreflexes and mechanoreflexes. J Appl Physiol 69:407–418
Seals DR, Victor RG (1991) Regulation of muscle sympathetic nerve activity during exercise in humans. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 19:313–349. doi:10.1249/00003677-199101000-00009
Sinoway L, Prophet S (1990) Skeletal muscle metaboreceptor stimulation opposes peak metabolic vasodilation in humans. Circ Res 66:1576–1584
Sinoway L, Prophet S, Gorman I, Mosher T, Shenberger J, Dolecki M, Briggs R, Zelis R (1989) Muscle acidosis during static exercise is associated with calf vasoconstriction. J Appl Physiol 66:429–436
Stenberg J, Astrand PO, Ekblom B, Royce J, Saltin B (1967) Hemodynamic response to work with different muscle groups, sitting and supine. J Appl Physiol 22:61–70
Stewart KJ, Bacher AC, Turner K, Lim JG, Hees PS, Shapiro EP, Tayback M, Ouyang P (2005) Exercise and risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome in older adults. Am J Prev Med 28:9–18. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2004.09.006
Sugawara J, Hayashi K, Yokoi T, Cortez-Cooper MY, DeVan AE, Anton MA, Tanaka H (2005) Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity: an index of central arterial stiffness? J Hum Hypertens 19:401–406. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001838
Sutton-Tyrrell K, Najjar SS, Boudreau RM, Venkitachalam L, Kupelian V, Simonsick EM, Havlik R, Lakatta EG, Spurgeon H, Kritchevsky S, Pahor M, Bauer D, Newman A, Health ABC Study (2005) Elevated aortic pulse wave velocity, a marker of arterial stiffness, predicts cardiovascular events in well-functioning older adults. Circulation 111:3384–3390. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.483628
Tanimoto M, Sanada K, Yamamoto K, Kawano H, Gando Y, Tabata I, Ishii N, Miyachi M (2008) Effects of whole-body low-intensity resistance training with slow movement and tonic force generation on muscular size and strength in young men. J Strength Cond Res 22:1926–1938
Tomiyama H, Yamashina A, Arai T, Hirose K, Koji Y, Chikamori T, Hori S, Yamamoto Y, Doba N, Hinohara S (2003) Influences of age and gender on results of noninvasive brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity measurement—a survey of 12517 subjects. Atherosclerosis 166:303–309. doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(02)00332-5
Volianitis S, Secher NH (2002) Arm blood flow and metabolism during arm and combined arm and leg exercise in humans. J Physiol 544:977–984. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.023556
Volianitis S, Krustrup P, Dawson E, Secher NH (2003) Arm blood flow and oxygenation on the transition from arm to combined arm and leg exercise in humans. J Physiol 547:641–648. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.034496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okamoto, T., Masuhara, M. & Ikuta, K. Upper but not lower limb resistance training increases arterial stiffness in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 107, 127–134 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1110-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1110-x