Abstract
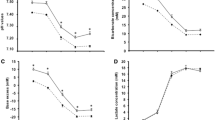
The extracellular pH defense against the lactic acidosis resulting from exercise can be estimated from the ratios −Δ[La] · ΔpH−1 (where Δ[La] is change in lactic acid concentration and ΔpH is change in pH) and Δ[HCO3 −] · ΔpH−1 (where Δ[HCO3 −] is change in bicarbonate concentration) in blood plasma. The difference between −Δ[La] · ΔpH−1 and Δ[HCO3 −] · ΔpH−1 yields the capacity of available non-bicarbonate buffers (mainly hemoglobin). In turn, Δ[HCO3 −] · ΔpH−1 can be separated into a pure bicarbonate buffering (as calculated at constant carbon dioxide tension) and a hyperventilation effect. These quantities were measured in 12 mountaineers during incremental exercise tests before, and 7–8 days (group 1) or 11–12 days (group 2) after their return from a Himalayan expedition (2800–7600 m altitude) under conditions of normoxia and acute hypoxia. In normoxia −Δ[La] · ΔpH−1 amounted to [mean (SEM)] 92 (6) mmol · l−1 before altitude, of which 19 (4), 48 (1) and 25 (3) mmol · l−1 were due to hyperventilation, bicarbonate and non-bicarbonate buffering, respectively. After altitude −Δ[La] · ΔpH−1 was increased to 128 (12) mmol · l−1 (P < 0.01) in group 1 and decreased to 72 (5) mmol · l−1 in group 2 (P < 0.05), resulting mainly from apparent large changes of non-bicarbonate buffer capacity, which amounted to 49 (14) mmol · l−1 in group 1 and to 10 (2) mmol · l−1 in group 2. In acute hypoxia the apparent increase in non-bicarbonate buffers of group 1 was even larger [140 (18) mmol · l−1]. Since the hemoglobin mass was only modestly elevated after descent, other factors must play a role. It is proposed here that the transport of La− and H+ across cell membranes is differently influenced by high-altitude acclimatization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 14 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böning, D., Maassen, N., Thomas, A. et al. Extracellular pH defense against lactic acid in normoxia and hypoxia before and after a Himalayan expedition. Eur J Appl Physiol 84, 78–86 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210000335
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210000335