Abstract
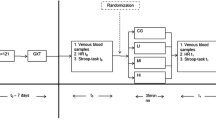
The neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) has been shown to modulate various physiological and psychological functions such as fatigue. Altered regulation of the serotonergic system has been suggested to play a role in response to exercise stress. In the present study, the influence was investigated of acute endurance exercise and short-term increase in the amount of training on the concentrations of the 5-HT precursor tryptophan (TRP), of prolactin (PRL) and of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) in the blood, as well as on the binding of [3H]ketanserin to the serotonin-2A (5-HT2A) receptors on platelets. Nine healthy endurance-trained men were tested the day before (I) and after (II) a 9-day training programme. Samples of venous blood were drawn after an overnight fast and following 5 h of cycling. Fasted and post-exercise plasma concentrations of free TRP, BCAA and free TRP:BCAA ratio did not differ between I and II. A significant decrease of plasma BCAA (P < 0.01) and significant augmentations of plasma free TRP, free TRP:BCAA ratio and PRL (P < 0.01) were found post-exercise. The increase in plasma PRL was smaller in II compared with I. Acute endurance exercise reduced the density of platelet 5-HT2A receptor [3H]ketanserin binding sites at I and II (P < 0.05). The basal density of the binding sites and the affinity of [3H]ketanserin for these binding sites were unaffected by an increase in the amount of training. The present results support the hypothesis that acute endurance exercise may increase 5-HT availability. This was reflected in the periphery by increased concentration of the 5-HT precursor free TRP, by increased plasma PRL concentration, and by a reduction of 5-HT2A receptors on platelets. It remains to be resolved whether these alterations in the periphery occur in parallel with an increase in the availability of 5-HT in the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 20 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strüder, H., Hollmann, W., Platen, P. et al. Effect of acute and chronic exercise on plasma amino acids and prolactin concentrations and on [3H]ketanserin binding to serotonin2A receptors on human platelets. Eur J Appl Physiol 79, 318–324 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050514
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050514