Abstract
Background
Intradialytic exercise has been poorly investigated in pediatric patients on chronic hemodialysis (HD). The aim of this study was to assess the acceptability, safety and efficacy of intradialytic exercise in children and young adults on HD.
Methods
The intradialytic exercise program consisted of 30-min sessions of intra-HD exercise using a cycloergometer two to three times a week for 3 months. Study endpoints were the 6-min walking test (6MWT) distances, lung function, number of stands in the chair test, lower extremity strength (LES), anthropometry, dietary intake, dialysis adequacy, incidence of symptomatic sessions, biochemistry and left ventricular mass index.
Results
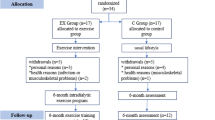
Ten pediatric patients with a median age of 15.3 (range 9.1–24.2) years were enrolled. Two of these underwent kidney transplantation; the remaining eight completed the study and adapted well to the exercise program. At the end of the 3-month study period, all patients had significantly improved results for the 6MWT (+4.9 %; p < 0.05), chair test (+19 %; p < 0.05) and LES (+29.3 %; p < 0.05). Pre-HD albumin, creatinine and total protein levels and post-HD creatinine levels had also significantly improved. The incidence of symptomatic sessions did not increase during the study period. No adverse events occurred.
Conclusions
Based on our results, we conclude that a 30-min exercise program of intradialytic cycling is feasible for the majority of pediatric patients on chronic HD and will be well accepted. Such an exercise program can lead to a significant improvement in the exercise capacity of this patient population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaar B, Feldkötter M, Nonn JM, Hoppe B (2011) Cardiorespiratory capacity in children and adolescents on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(11):3701–3708
Zanconato S, Baraldi E, Montini G, Zacchello G, Zacchello F (1990) Exercise tolerance in end-stage renal disease. Child Nephrol Urol 10(1):26–31
Baraldi E, Montini G, Zanconato S, Zacchello G, Zacchello F (1990) Exercise tolerance after anaemia correction with recombinant human erythropoietin in end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 4(6):623–626
Pattaragarn A, Warady BA, Sabath RJ (2004) Exercise capacity in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Perit Dial Int 24(3):274–280
Bonzel KE, Wildi B, Weiss M, Scharer K (1991) Spiroergometric performance of children and adolescents with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 5(1):22–28
Painter P, Krasnoff J, Mathias R (2007) Exercise capacity and physical fitness in pediatric dialysis and kidney transplant patients. Pediatr Nephrol 22(7):1030–1039
Alayli G, Ozkaya O, Bek K, Calmasur A, Diren B, Bek Y, Canturk F (2008) Physical function, muscle strength and muscle mass in children on peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 23(4):639–644
Weaver DJ Jr, Kimball TR, Knilans T, Mays W, Knecht SK, Gerdes YM, Witt S, Glascock BJ, Kartal J, Khoury P, Mitsnefes MM (2008) Decreased maximal aerobic capacity in pediatric chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(3):624–630
Takken T, Engelbert E, van Bergen M, Groothoff J, Nauta J, van Hoeck K, Lilien M, Helders P (2009) Six-minute walking test in children with ESRD: discrimination validity and construct validity. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2217–2223
Eijsermans RM, Creemers DG, Helders PJ, Schröder CH (2004) Motor performance, exercise tolerance, and health-related quality of life in children on dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 19(11):1262–1266
Goldstein SL (2009) Physical functioning in children with end-stage renal disease: small steps first. Pediatr Transplant 13(7):802–804
Clapp EL, Bevington A, Smith AC (2012) Exercise for children with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 27(2):165–172
Goldstein SL (2009) Physical fitness in children with end-stage renal disease. Adv Chron Kidney Dis 16(6):430–436
Konstantinidou E, Koukouvou G, Kouidi E, Deligiannis A, Tourkantonis A (2002) Exercise training in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis: comparison of three rehabilitation programs. Clin Nephrol 61[Suppl 1]:S31–S38
Storer TW, Casaburi R, Sawelson S, Kopple JD (2005) Endurance exercise training during haemodialysis improves strength, power, fatigability and physical performance in maintenance haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(7):1429–1437
Petersen AC, Leikis MJ, McMahon LP, Kent AB, McKenna MJ (2009) Effects of endurance training on extrarenal potassium regulation and exercise performance in patients on haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(9):2882–2888
Heiwe S, Jacobson SH (2011) Exercise training for adults with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5: CD003236
Kosmadakis GC, Bevington A, Smith AC, Clapp EL, Viana JL, Bishop NC, Feehally J (2010) Physical exercise in patients with severe kidney disease. Nephron Clin Pract 115(1):c7–c16
Giannaki CD, Stefanidis I, Karatzaferi C, Liakos N, Roka V, Ntente I, Sakkas GK (2011) The effect of prolonged intradialytic exercise in hemodialysis efficiency indices. ASAIO J 57(3):213–218
Smart N, Steele M (2011) Exercise training in haemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrology (Carlton) 16(7):626–632
Cheema B, Abas H, Smith B, O'Sullivan A, Chan M, Patwardhan A, Kelly J, Gillin A, Pang G, Lloyd B, Singh MF (2007) Progressive exercise for anabolism in kidney disease (PEAK): a randomized, controlled trial of resistance training during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(5):1594–1601
Wilund KR, Tomayko EJ, Wu PT, Ryong Chung H, Vallurupalli S, Lakshminarayanan B, Fernhall B (2010) Intradialytic exercise training reduces oxidative stress and epicardial fat: a pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25(8):2695–2701
Ouzouni S, Kouidi E, Sioulis A, Grekas D, Deligiannis A (2009) Effects of intradialytic exercise training on health-related quality of life indices in haemodialysis patients. Clin Rehabil 23(1):53–63
Parsons TL, Toffelmire EB, King-VanVlack CE (2004) The effect of an exercise program during hemodialysis on dialysis efficacy, blood pressure and quality of life in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. Clin Nephrol 61(4):261–274
Anderson JE, Boivin MR Jr, Hatchett L (2004) Effect of exercise training on interdialytic ambulatory and treatment-related blood pressure in hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail 26(5):539–544
Majchrzak KM, Pupim LB, Flakoll PJ, Ikizler TA (2008) Resistance exercise augments the acute anabolic effects of intradialytic oral nutritional supplementation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23(4):1362–1369
Mustata S, Chan C, Lai V, Miller JA (2004) Impact of an exercise program on arterial stiffness and insulin resistance in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(10):2713–2718
Kouidi EJ, Grekas DM, Deligiannis AP (2009) Effects of exercise training on noninvasive cardiac measures in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 54(3):511–521
Segura-Ortí E, Kouidi E, Lisón JF (2009) Effect of resistance exercise during hemodialysis on physical function and quality of life: randomized controlled trial. Clin Nephrol 71(5):527–537
Kopple JD, Wang H, Casaburi R, Fournier M, Lewis MI, Taylor W, Storer TW (2007) Exercise in maintenance hemodialysis patients induces transcriptional changes in genes favoring anabolic muscle. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(11):2975–2986
Pupim LB, Flakoll PJ, Ikizler TA (2007) Exercise improves albumin fractional synthetic rate in chronic hemodialysis patients. Eur J Clin Nutr 61(5):686–689
Vaithilingam I, Polkinghorne KR, Atkins RC, Kerr PG (2004) Time and exercise improve phosphate removal in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 43(1):85–89
Kong CH, Tattersall JE, Greenwood RN, Farrington K (1999) The effect of exercise during haemodialysis on solute removal. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(12):2927–2931
van Bergen M, Takken T, Engelbert R, Groothoff J, Nauta J, van Hoeck K, Helders P, Lilien M (2009) Exercise training in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 24:619–622
Goldstein SL, Montgomery LR (2009) A pilot study of twice-weekly exercise during hemodialysis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:833–839
Miller MR, Crapo R, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Enright P, van der Grinten CP, Gustafsson P, Jensen R, Johnson DC, MacIntyre N, McKay R, Navajas D, Pedersen OF, Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Wanger J, ATS/ERS Task Force (2005) General considerations for lung function testing. Eur Respir J 26(1):153–161
ATS/ERS Task Force (2005) Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 26(2):319–338
Frisancho AR (1981) New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 34:2540–2545
Daniels SR, Kimball TR, Morrison JA, Khoury P, Meyers RA (1995) Indexing left ventricular mass to account for differences in body size in children and adolescents without cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 76:699–701
Paglialonga F, Lopopolo A, Scarfia RV, Galli MA, Brivio A, Grassi MR, Salera S, Edefonti A (2013) Correlates of exercise capacity in pediatric patients on chronic hemodialysis. J Ren Nutr 23(5):380–386
Sietsema KE, Hiatt WR, Esler A, Adler S, Amato A, Brass EP (2002) Clinical and demographic predictors of exercise capacity in end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 39(1):76–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paglialonga, F., Lopopolo, A., Scarfia, R.V. et al. Intradialytic cycling in children and young adults on chronic hemodialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 29, 431–438 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2675-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2675-5